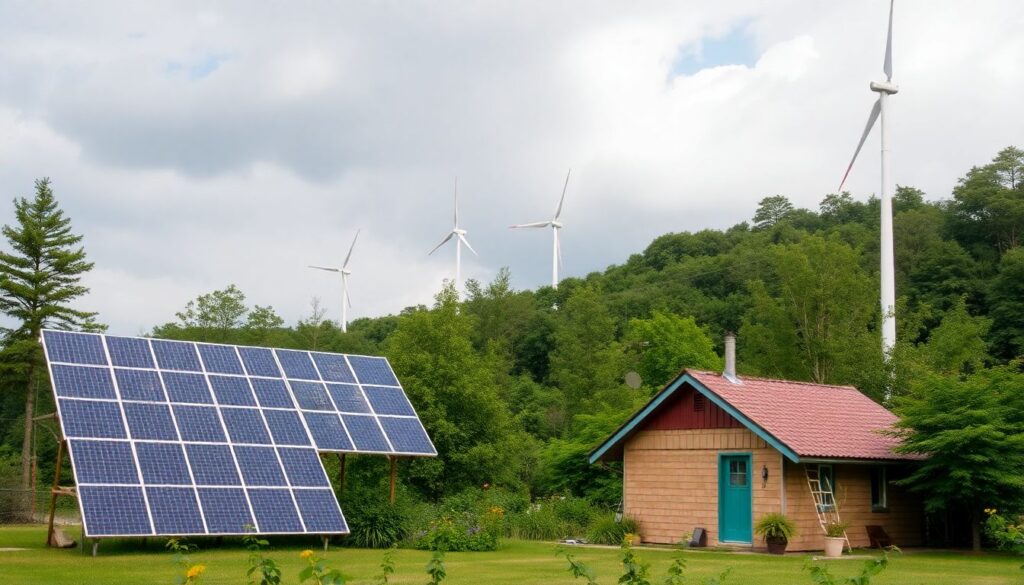
In a world where the grid can flicker and fail, and the cost of traditional energy sources continues to rise, have you ever wondered how you could power your life off the grid, sustainably, and independently? Welcome to ‘The Prepper’s Guide to Alternative Energy Sources’, your comprehensive roadmap to harnessing the power of nature and technology to meet your energy needs. But before we dive into the fascinating world of alternative energy, let’s take a moment to appreciate the magnitude of our dependence on electricity. Did you know that the average American home consumes over 900 kilowatt-hours of electricity per month? That’s enough to power a small town in some parts of the world! Now, imagine if you could generate that power yourself, using nothing but the sun, the wind, or the earth’s geothermal heat. Sounds like a dream? It’s not. It’s a reality that thousands of people around the world are already living. But how do you get started? What are the best alternative energy sources for your needs? And how can you ensure that your off-grid power system is reliable, efficient, and sustainable? These are the questions we’ll be exploring in this guide. So, if you’re ready to take control of your energy future, read on. We promise to demystify the world of alternative energy, provide practical tips and real-life examples, and equip you with the knowledge and confidence to make informed decisions about your off-grid power needs. Let’s embark on this exciting journey together!
Powering Your Off-Grid Life: A Journey into Sustainable Living
Embarking on a journey into sustainable living is like setting sail on a ship powered by the wind and sun, navigating the vast ocean of life without relying on traditional grids. Imagine waking up each morning to the gentle hum of solar panels soaking up the sun’s energy, or the rhythmic spin of a wind turbine dancing with the breeze, generating electricity to fuel your day. This is not a life of scarcity, but one rich in ingenuity and self-sufficiency. It’s about harnessing the power of nature, from rainwater harvesting to composting, creating a harmonious cycle of waste reduction and resource conservation. It’s about embracing the rhythm of the seasons, eating fresh produce from your own garden, and understanding the true value of every drop of water and morsel of food. It’s about freedom
- from utility bills, from the constraints of conventional living, and from the guilt of excessive consumption. It’s about creating a life that’s not just sustainable, but regenerative, leaving a positive impact on the planet. So, let’s dive in, explore the possibilities, and power your off-grid life with sustainability and joy.
Understanding Alternative Energy
In the grand tapestry of our planet’s energy landscape, alternative energy sources stand out as a vibrant, sustainable thread. Alternative energy, often referred to as clean or green energy, encompasses a range of energy sources that are less harmful to the environment than traditional methods. These include solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass, among others. The importance of alternative energy cannot be overstated. It helps mitigate climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promotes energy independence, and creates new job opportunities in the green economy.
Preppers, individuals who prepare for potential disasters or emergencies, should consider alternative energy for several reasons. Firstly, it provides a reliable, off-grid power source in case of grid failures or natural disasters. Secondly, it can significantly reduce energy costs in the long run, freeing up resources for other preparedness efforts. Lastly, it aligns with the principle of self-sufficiency, a core value in the prepper community.
To understand alternative energy better, let’s differentiate it from its counterparts. Energy sources can be broadly categorized into two types: renewable and non-renewable.
Renewable energy sources, like the sun, wind, and water, are virtually inexhaustible and can replenish naturally over time. They are clean at the point of use, meaning they do not produce pollutants or greenhouse gases. Examples include solar panels, wind turbines, and hydroelectric power plants.
On the other hand, non-renewable energy sources, such as fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, are finite and formed over millions of years from the remains of ancient organisms. They are not only running out but also contribute significantly to air and water pollution, as well as climate change. Nuclear power, while not a fossil fuel, is also considered non-renewable due to the finite nature of its fuel source and the radioactive waste it produces.
In conclusion, understanding alternative energy is crucial in our quest for a sustainable future. It offers a clean, reliable, and cost-effective solution to our energy needs, making it an attractive option for both everyday use and emergency preparedness.

Solar Power: Harnessing the Sun’s Energy
In the grand tapestry of renewable energy sources, solar power stands as a beacon of promise and sustainability. Harnessing the sun’s boundless energy, it offers a clean, inexhaustible alternative to fossil fuels, making it an attractive option for both environmental enthusiasts and preppers alike. Let’s delve into the world of solar power, exploring its advantages and how it can be utilized to create self-sufficient, off-grid systems.Solar power is generated through the photovoltaic effect, a process by which sunlight is converted into direct current (DC) electricity. This is achieved through solar panels, which are composed of multiple photovoltaic cells. These cells, made of semiconducting materials, absorb photons of light and release electrons, creating a flow of electricity. The DC electricity produced can then be converted into alternating current (AC) electricity using an inverter, making it compatible with most household appliances.One of the primary advantages of solar power is its cost-effectiveness in the long run. While the initial investment for solar panels can be high, the cost of electricity generated is significantly lower than that from traditional sources. Moreover, solar power is a hedge against rising electricity prices, as once the system is installed, the cost of generating electricity is virtually zero. Additionally, solar power systems require minimal maintenance, further reducing long-term costs.Solar power also offers a high degree of independence and resilience, making it an excellent choice for preppers. By installing an off-grid solar system, one can reduce reliance on the public power grid, ensuring a steady supply of electricity even during power outages. These systems typically consist of solar panels, a charge controller, batteries for energy storage, and an inverter. The size and capacity of the system can be tailored to meet specific energy needs.Another innovative application of solar power is solar water heating. Solar water heaters use the sun’s energy to heat water, reducing the need for conventional water heaters that consume electricity or gas. These systems typically consist of solar collectors, a storage tank, and a heat exchanger. The solar collectors absorb the sun’s heat, transferring it to a heat transfer fluid, which then heats the water in the storage tank. This not only reduces energy consumption but also lowers greenhouse gas emissions.In conclusion, solar power offers a clean, cost-effective, and resilient source of energy that can be harnessed to meet a wide range of needs. Whether you’re looking to reduce your carbon footprint, save on energy costs, or prepare for off-grid living, solar power provides a viable and attractive solution. So, why not harness the sun’s energy and join the solar revolution?

Wind Power: Generating Energy from the Wind
Embracing the power of nature, wind power has emerged as a sustainable and increasingly popular method for off-grid living. Imagine harnessing the relentless energy of the wind to generate electricity, reducing your reliance on traditional power sources and minimizing your carbon footprint. The journey towards wind-powered independence begins with understanding the diverse types of wind turbines available.
At the heart of wind power lie two primary categories of turbines: Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT) and Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWT). HAWTs, the more common type, feature blades that rotate around a horizontal axis, much like a traditional windmill. They are efficient in high wind speeds and can generate significant power. VAWTs, on the other hand, have blades that rotate around a vertical axis, offering advantages like safety, noise reduction, and the ability to operate in lower wind speeds.
Installing a wind turbine involves several steps. First, you’ll need to assess your site’s wind resources using tools like wind maps or anemometers. Next, choose a turbine that suits your energy needs and wind conditions. Then, prepare your site by ensuring it’s accessible for installation and meets local regulations. Once ready, the turbine can be assembled and mounted, followed by connecting it to your electrical system.
Regular maintenance is crucial to keep your wind turbine running smoothly and prolong its lifespan. This includes inspecting the blades for damage, checking the gearbox and bearings for wear, and ensuring the electrical components are functioning correctly. Safety checks, such as securing the tower and lubricating moving parts, are also essential. By staying on top of these tasks, you’ll ensure your wind turbine continues to generate clean, reliable energy for years to come.
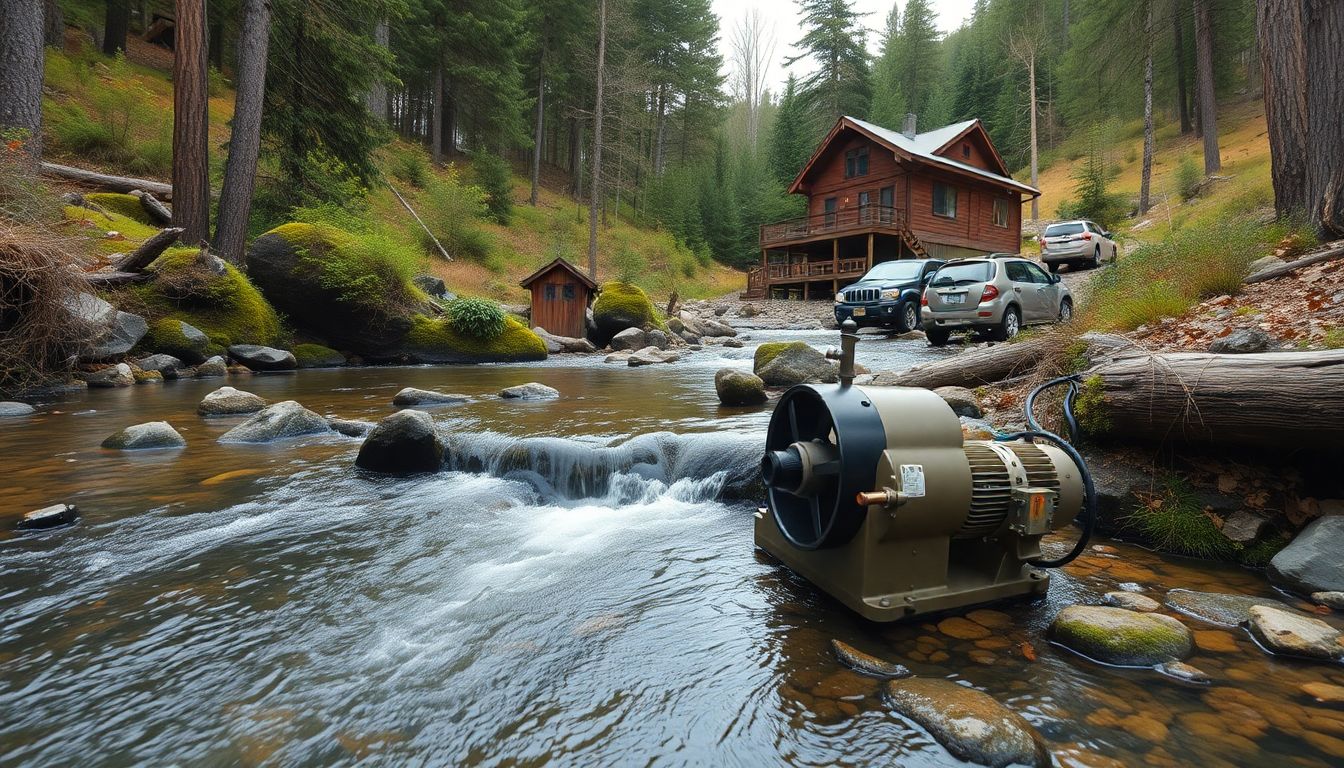

Hydropower: Generating Energy from Water
In the realm of off-grid living and preparedness, hydropower often takes a backseat to solar and wind energy. However, for those with access to a reliable water source, hydropower presents a unique opportunity to generate clean, renewable energy. This is where micro-hydro setups come into play.
Micro-hydro systems are small-scale hydropower installations designed for homes, cabins, or remote communities. They harness the energy from moving water, typically from a stream or river, to generate electricity. The setup involves a turbine, a generator, and a control system. The turbine converts the kinetic energy of the water into mechanical energy, which is then converted into electrical energy by the generator.
Installing a micro-hydro system is a multi-step process. First, you need to assess your water source. The ideal setup has a consistent water flow and a significant drop in elevation. Next, you’ll need to choose the right turbine and generator for your water flow rate. The installation process involves setting up an intake pipe to direct water to the turbine, ensuring the turbine and generator are securely mounted, and running the electrical wiring to your home.
Once installed, maintaining a micro-hydro system is relatively straightforward. Regular checks for debris buildup in the intake pipe and turbine are crucial to prevent damage. Annual inspections of the turbine and generator can help identify any wear and tear. Additionally, keeping an eye on the electrical components, such as the wiring and control system, can ensure the system’s longevity.
In conclusion, while hydropower might not be the first choice for preppers, it’s a viable and sustainable option for those with access to a reliable water source. Micro-hydro setups, with their relatively simple installation and maintenance, can provide a consistent source of off-grid electricity.

Geothermal Energy: Tapping into the Earth’s Heat
Imagine harnessing the Earth’s internal heat, a renewable resource that’s been keeping our planet warm since its inception. Welcome to the world of geothermal energy, a clean, sustainable, and increasingly popular option for off-grid living. Geothermal energy is derived from the Greek words ‘geo,’ meaning earth, and ‘therme,’ meaning heat. It’s a testament to human ingenuity, tapping into the Earth’s core where temperatures can reach up to 9,000°F (4,950°C).
At its core, geothermal energy is about moving heat from one place to another. This is where geothermal heat pumps (GHPs) come into play. They’re essentially heat exchangers, transferring heat from the Earth to your home in the winter, and vice versa in the summer. Think of it like a heat pump on steroids, using the Earth’s stable temperature as its heat source and sink.
Installing a GHP involves several steps. First, you’ll need to determine the best system for your property. Closed-loop systems circulate a heat transfer fluid through pipes buried underground, while open-loop systems use groundwater directly. Next, you’ll need to install the ground loop, which can be done horizontally or vertically, depending on your property size and soil conditions. Once the loop is in place, the heat pump can be installed indoors, connecting to your existing ductwork or radiant heating system.
One of the most appealing aspects of GHPs is their efficiency. Because they’re moving heat rather than generating it, they can achieve up to four units of heat for every unit of electricity used. This makes them an excellent choice for off-grid living, where energy efficiency is paramount. Plus, they provide both heating and cooling, making them a versatile investment.
But geothermal energy isn’t just about heating and cooling. It can also be used to generate electricity, a process known as geothermal power. This involves drilling deep into the Earth to access hot water or steam, which is then used to drive a turbine and generate electricity. While this requires more infrastructure and isn’t typically feasible for off-grid living, it’s a promising avenue for larger-scale renewable energy production.
In conclusion, geothermal energy is a powerful tool for off-grid living, offering a clean, efficient, and sustainable way to heat and cool your home. With geothermal heat pumps, you’re not just tapping into the Earth’s heat, you’re harnessing a resource that’s been powering our planet for billions of years. So why not put it to work for you?

Biogas: Converting Waste into Energy
In the realm of sustainable energy, biogas stands as a shining example of turning waste into a valuable resource. For preppers and eco-conscious individuals, generating energy from organic waste is not only a practical way to reduce dependence on traditional power sources but also a step towards a greener, more self-sufficient lifestyle.
The process of biogas production, also known as anaerobic digestion, is a natural one. It involves the breakdown of organic material by bacteria in the absence of oxygen. This process can occur in a variety of environments, from landfills to dedicated biogas plants, and even in your backyard.
To set up a biogas system at home, you’ll need a few key pieces of equipment. The most important is a biogas digester, a sealed tank where the anaerobic digestion process takes place. This can be as simple as an underground pit or as complex as a high-tech, insulated tank. Other equipment includes a gas collector, which captures the biogas as it’s produced, and a gas stove or generator to use the biogas.
But biogas production isn’t just about setting it and forgetting it. Maintenance is key to keeping your system running smoothly. This includes regularly adding organic waste to feed the bacteria, monitoring the pH levels to ensure they’re within the bacteria’s comfort zone, and occasionally cleaning the digester to remove any buildup.
So, what can you use to feed your biogas system? The possibilities are vast. Food scraps, yard waste, even manure from your livestock can all be used to produce biogas. Just remember, the more diverse the organic material, the more efficient the digestion process will be.
In essence, biogas is a testament to the power of nature and human ingenuity. It’s a reminder that waste isn’t something to be discarded, but a resource to be harnessed. So, why not give it a try? With a little effort and the right equipment, you too can convert waste into energy and take a step towards a more sustainable future.

Energy Storage: Powering Your Life Off-Grid
Embarking on an off-grid lifestyle, one of the first questions that arises is: how do I power my life without being connected to the main grid? The answer lies in the heart of energy storage. Imagine living in a world where you’re not tied down to a power outlet, where you can take your energy with you, and where you’re not at the mercy of power outages. This is the world of off-grid living, powered by energy storage systems. Energy storage, in essence, is the key to unlocking the full potential of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. It allows you to capture energy when it’s abundant and use it when you need it most. But with so many types of batteries available, choosing the right one can be a daunting task. Let’s dive into the world of batteries. There are three main types: lead-acid, nickel-based, and lithium-ion. Lead-acid batteries are the most common, known for their low cost and high power output. However, they have a shorter lifespan and require regular maintenance. Nickel-based batteries, on the other hand, have a longer lifespan but are more expensive. Lithium-ion batteries, the latest addition to the family, offer the best of both worlds: high power output, long lifespan, and low maintenance. But they come at a premium price. Maintenance is crucial to extend the lifespan of your batteries. For lead-acid batteries, this involves regular equalization charging to prevent sulfation, and periodic checks of the electrolyte levels. Nickel-based batteries require less maintenance, but their lifespan can be affected by deep discharges. Lithium-ion batteries, being sealed, require no maintenance, but they are sensitive to high temperatures. The lifespan of a battery is measured in cycles, with one cycle being a full discharge and recharge. Lead-acid batteries typically last between 300 to 1000 cycles, nickel-based between 500 to 2000 cycles, and lithium-ion between 1000 to 5000 cycles. However, these numbers can vary greatly depending on the depth of discharge, temperature, and the quality of the battery. In conclusion, energy storage is not just a convenience in off-grid living; it’s a necessity. It allows you to harness the power of nature and use it to your advantage. Whether you choose lead-acid, nickel-based, or lithium-ion batteries, understanding their maintenance and lifespan will help you make the most out of your off-grid energy storage system.

Energy Efficient Appliances: Reducing Your Power Needs
In the realm of off-grid living, every watt counts. Energy-efficient appliances are not just a luxury, but a necessity. They help reduce your power needs, allowing you to make the most of your renewable energy sources and maintain a sustainable lifestyle.
Take, for instance, the humble refrigerator. An energy-efficient model can consume up to 50% less power than its conventional counterpart. This means you can spend less time worrying about keeping your food fresh and more time enjoying it. Some top-rated energy-efficient refrigerators include the Samsung RF28R7201SR and the LG LRFVS3006S.
When choosing energy-efficient appliances, look for the Energy Star label. This international standard helps you identify products that meet strict energy efficiency guidelines. Here are some tips to guide your selection:
- Check the Energy Guide label. This provides an estimate of the appliance’s annual energy consumption and compares it to similar models.
- Consider the size and capacity. Larger appliances generally consume more energy, so choose a size that suits your needs.
- Look for features like auto-off, energy-saving modes, and smart controls. These can help you further reduce energy consumption.
- Think long-term. Energy-efficient appliances may have a higher upfront cost, but they can save you money in the long run through lower energy bills.
Other appliances to consider include energy-efficient washing machines, dishwashers, and lighting solutions. LED bulbs, for example, use up to 75% less energy than incandescent bulbs and last up to 25 times longer.
By investing in energy-efficient appliances, you’re not just reducing your power needs, you’re also contributing to a cleaner, more sustainable environment. It’s a win-win situation that’s perfect for off-grid living.
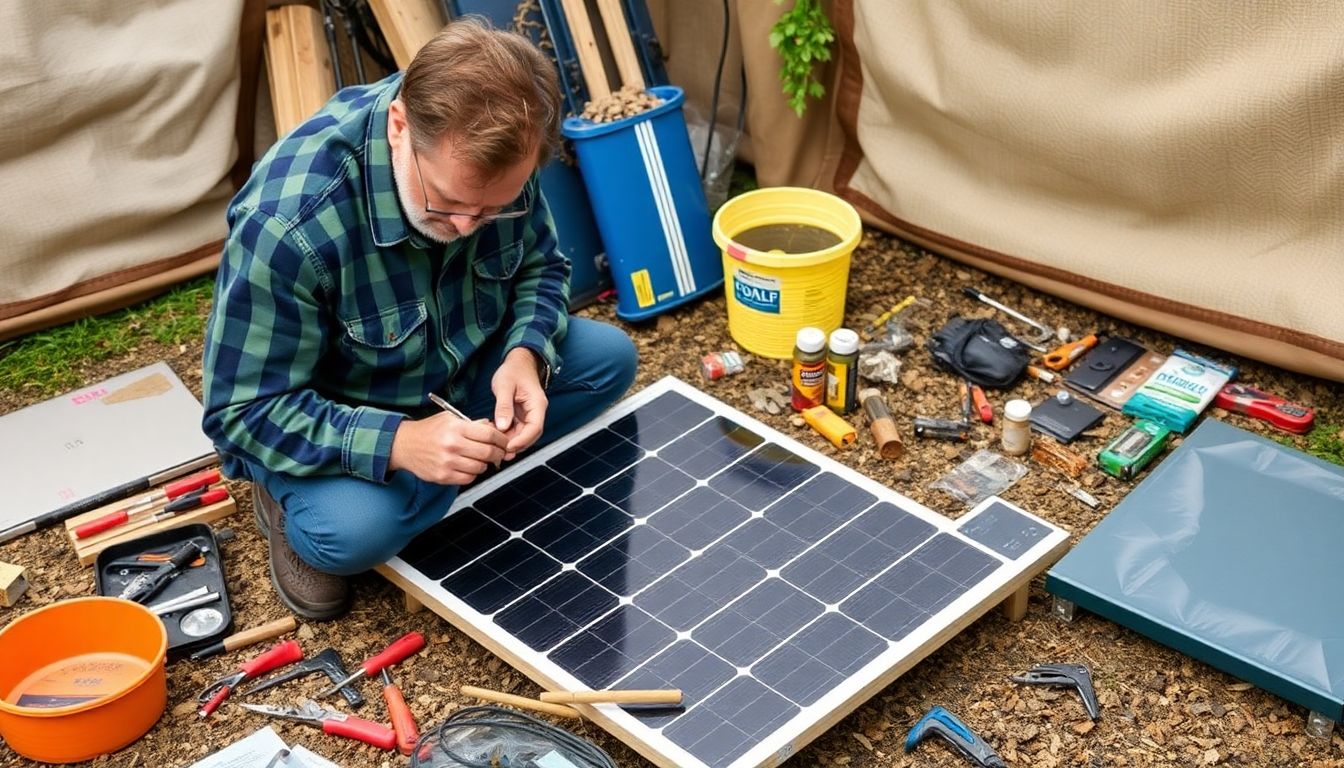

DIY Energy Projects: Saving Money and Building Skills
Embarking on DIY energy projects is not only a rewarding way to save money but also an excellent opportunity to learn new skills and become more self-sufficient. These projects, often favored by preppers, range from simple to complex, catering to various skill levels and needs. Let’s delve into some of these projects, their benefits, and the challenges they present.
The humble solar oven is a great starting point. It’s easy to build using materials like cardboard, aluminum foil, and plastic wrap. The sun’s energy is harnessed to heat food, making it an eco-friendly and cost-effective alternative to conventional ovens. However, it’s important to note that it’s weather-dependent and not suitable for cooking large meals or in cloudy conditions.
Wind turbines are another fascinating DIY energy project. They can generate electricity using wind power, reducing your reliance on the grid. Building a small-scale turbine can be a rewarding challenge, teaching you about aerodynamics and renewable energy. However, they require consistent wind speeds and can be noisy, which might not make them suitable for all locations.
For those with a knack for electronics, building a DIY solar panel can be an enlightening experience. It involves understanding the principles of photovoltaic cells and can save you money in the long run. The challenge lies in sourcing the right materials and ensuring the panel’s longevity.
Installing a rainwater harvesting system is another beneficial project. It collects and stores rainwater for later use, reducing your water bills and helping the environment. The system can be as simple as a barrel under a downspout or as complex as an underground tank with a pump. However, it requires careful planning to ensure the water is clean and safe for use.
While these projects offer numerous benefits, they also come with challenges. They require time, patience, and often, a learning curve. They might also need permits or adherence to local regulations. But with each challenge overcome, you’ll gain new skills and a sense of accomplishment. Moreover, you’ll be contributing to a more sustainable future, one DIY project at a time.

Legal and Safety Considerations for Off-Grid Energy
Embarking on an off-grid energy journey is an exciting step towards sustainability and independence. However, it’s crucial to navigate the legal and safety aspects with care to ensure a smooth and secure transition. Let’s delve into these considerations, one step at a time.
The first port of call is understanding and obtaining the necessary permits. Off-grid energy systems often involve renewable sources like solar or wind, which may require permits from local authorities or planning departments. These permits ensure your system complies with building codes and zoning regulations, preventing any legal hiccups down the line. It’s always wise to consult with local officials or hire a professional to guide you through this process.
Next, let’s talk about insurance. While off-grid energy systems can reduce your carbon footprint, they can also increase your liability. It’s essential to review your homeowner’s insurance policy to ensure it covers potential damages or injuries related to your off-grid system. If not, consider adding an endorsement or purchasing separate coverage. After all, safety and security should never be an afterthought.
Now, let’s shift our focus to safety precautions. Off-grid energy systems, particularly those involving electricity, can pose hazards if not installed and maintained correctly. Here are some safety steps to keep in mind:
- Always hire a licensed electrician to install your system to ensure it meets safety standards.
- Regularly inspect and maintain your system to prevent malfunctions.
- Install safety features like automatic shut-off switches and ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs).
- Ensure your system is properly grounded to prevent electrical shocks.
- Store and handle energy sources safely, following manufacturer guidelines.
By adhering to these legal and safety considerations, you’re not just protecting yourself and your investment, but also ensuring a sustainable and responsible off-grid energy future.
FAQ
What is the primary goal of exploring alternative energy sources for preppers and off-grid enthusiasts?
Which alternative energy sources are most suitable for off-grid living?
How does solar power work, and what are the key components of a solar energy system?
What factors should be considered when determining the size of an off-grid solar power system?
How can wind power be harnessed for off-grid living, and what are the considerations for installing a wind turbine?
- Average wind speed in the location – turbines require consistent wind speeds to generate meaningful power.
- Tower height – taller towers can access stronger and more consistent winds but require more investment and maintenance.
- Turbine size – larger turbines generate more power but may require more space and infrastructure.
- Grid interconnection or off-grid use – determine if the turbine will feed power into the grid or supply an off-grid home.
- Noise and environmental impact – consider the noise levels and potential impact on local wildlife.









