Dive into the captivating and urgent story of Alaska’s changing landscape, where melting glaciers and extreme weather events are reshaping the region. This article explores the dire warnings issued by scientists and the innovative solutions being implemented to combat these challenges.
From rising temperatures to shrinking salmon populations, Alaska faces unprecedented challenges. Discover the alarming findings and the innovative solutions being implemented.
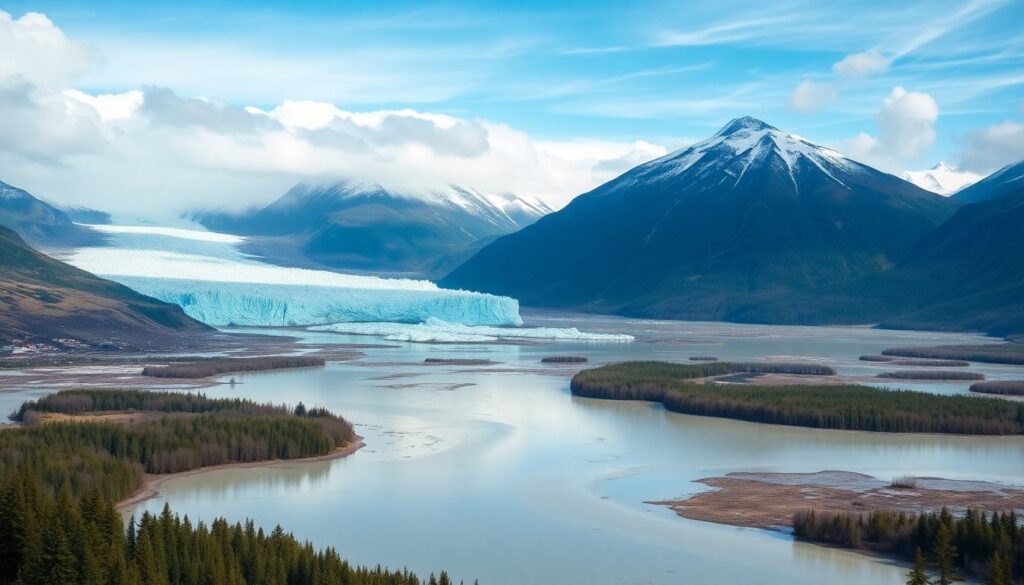
Imagine the vast, untamed wilderness of Alaska, where towering mountains kiss the sky and glaciers carve their way through the landscape. These icy giants, once formidable and eternal, are now retreating, leaving behind stark rock and flooded valleys. The once-frozen rivers of ice, now melt, feeding the hungry sea, and forever altering the landscape.
Picture the crystal-clear waters of Alaska’s rivers and streams, teeming with life, from the mighty salmon to the humble algae. But this vibrant underwater world is under threat. Warming waters and altered currents wreak havoc on delicate ecosystems, causing fish to struggle to find their way back to their natal streams, and leaving fisheries in a state of flux.
Alaska’s natural beauty is a sight to behold, but the impacts of climate change are devastating. As the glaciers melt, sea levels rise, flooding coastal areas and transforming the landscape into something almost unrecognizable. The contrast between the stunning natural beauty and the stark reality of climate change is jarring, serving as a stark reminder of the urgent need for action.

The Changing Landscape of Alaska
The Alaska Center for Climate Assessment and Policy has recently revealed some alarming findings, shedding light on the profound impact of climate change on the state. The research underscores the drastic effects of melting glaciers and extreme weather events, which are becoming increasingly frequent and severe. These phenomena are not just reshaping Alaska’s iconic landscapes but also posing significant challenges to its communities and ecosystems.
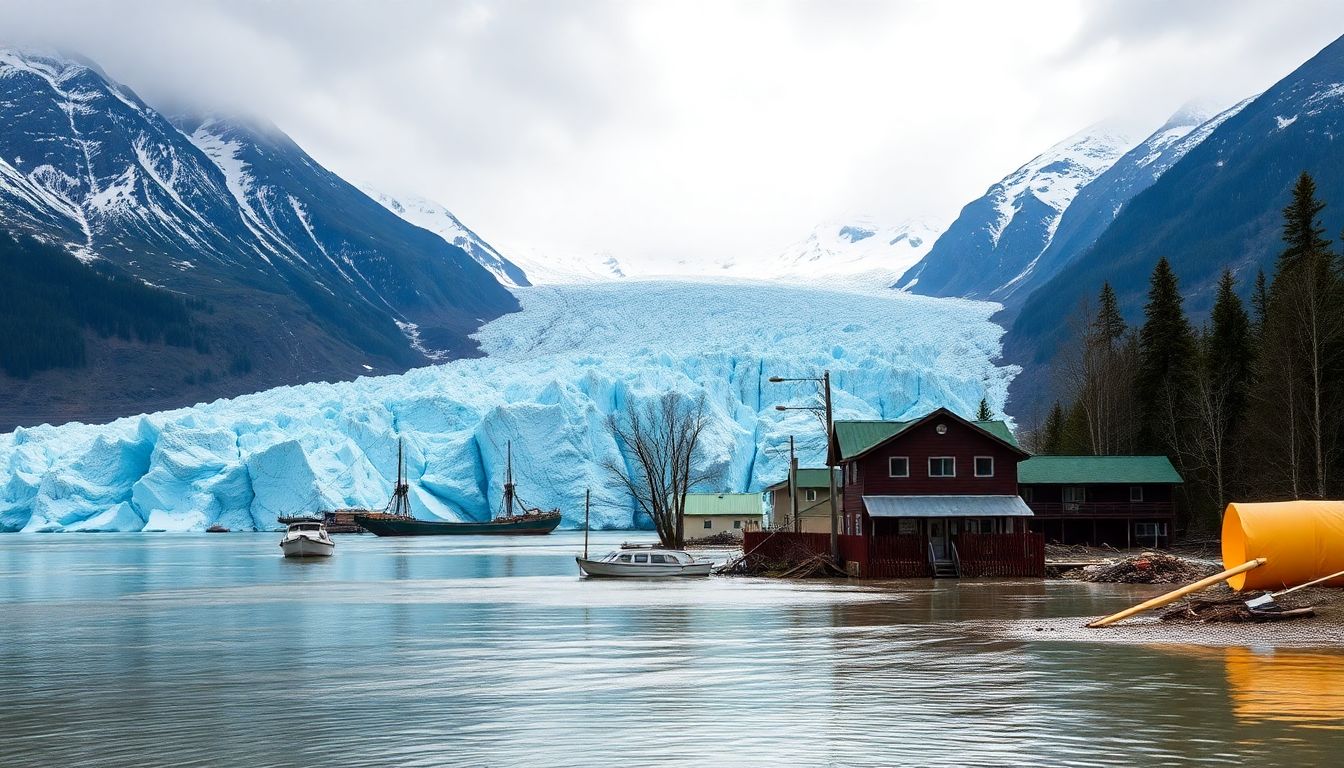
One of the most striking examples of these changes is the long-term thinning of the Mendenhall Glacier. This magnificent glacier, a major attraction near Juneau, has been retreating at an unprecedented rate. According to the center’s reports, the glacier has receded by over 1.75 miles since the mid-1700s, with the rate of retreat accelerating in recent decades. This thinning is not just a loss of ice; it signifies a profound disruption in the local ecosystem, affecting everything from wildlife habitats to river flows.
The impact of melting glaciers is not confined to the wilderness. Juneau, Alaska’s capital, is experiencing firsthand the consequences of this rapid environmental change. In recent years, the city has faced severe flooding, exacerbated by the increased meltwater from surrounding glaciers. The Alaska Center for Climate Assessment and Policy has highlighted how these floods are becoming more frequent and intense, posing significant threats to infrastructure, homes, and businesses. Some of the key impacts include:
- Damage to roads and buildings, disrupting daily life and resulting in costly repairs.
- Changes in water quality and availability, affecting local communities and wildlife.
- Increased risk of landslides and erosion, further altering the landscape and endangering residents.

Extreme Weather and Its Impact
In the vast, untamed wilderness of Alaska, extreme weather events have been shaping the landscape and challenging local communities with increasing ferocity. One of the most notable recent events is Typhoon Merbok, which made its presence known in September 2022. Merbok was an unusual and powerful storm, remnant of the typhoon which took shape in the West Pacific. Merbok battered the western coast of Alaska with hurricane-force winds and massive storm surges, causing severe coastal erosion and flooding.
The impacts of Typhoon Merbok were devastating for local communities. Villages like Golovin and Newtok faced monumental storm surges, leading to significant infrastructure damage and displacement of residents. The storm’s ferocity was not an isolated incident; it’s part of a broader trend of intensifying storms and extreme weather events linked to climate change. As global temperatures rise, the atmosphere can hold more moisture, leading to more frequent and intense storms. Additionally, warming oceans fuel stronger and more frequent typhoons and hurricanes.
Alongside intense storms, Alaska has witnessed an increase in deadly landslides, another phenomenon exacerbated by climate change. In October 2020, a catastrophic landslide occurred in Haines, claiming lives and causing extensive damage. As permafrost thaws due to rising temperatures, the landscape becomes more unstable, increasing the risk of landslides. These events highlight the cascading effects of climate change on Alaska’s geology and topography.
The impacts of these events on local communities are profound and multifaceted:
- Infrastructure Damage: Homes, roads, and critical infrastructure are destroyed or severely damaged, disrupting daily life and communication.
- Economic Loss: Fishing, tourism, and other local industries suffer significant setbacks, affecting livelihoods.
- Cultural Erosion: The loss of traditional lands and historic sites threatens cultural heritage and identity.
- Displacement: Residents are forced to relocate, often leading to social and emotional upheaval.
- Safety and Health Concerns: Extreme events pose immediate risks to life and long-term health impacts due to stress, injury, and disrupted healthcare services.
Understanding the link between these extreme weather events and climate change is crucial for mitigation efforts and building resilience in Alaska’s communities.

Alaska’s Fisheries in Crisis
In the pristine waters of Alaska, a silent struggle is unfolding. Marine heat waves, periods of unusually high ocean temperatures, are wreaking havoc on the state’s fisheries. These heat waves, exacerbated by climate change, are causing significant shifts in fish populations. Sockeye salmon, a keystone species, are moving to colder waters, disrupting traditional migration patterns. Meanwhile, warmer waters are causing increased mortality rates among juvenile fish, leading to smaller adult populations. Additionally, changes in ocean currents are bringing in warm water species, disrupting the delicate balance of Alaska’s marine ecosystems.
Ocean acidification, often dubbed ‘climate change’s evil twin,’ presents another formidable challenge. As the ocean absorbs excess carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, it becomes more acidic, making it harder for marine organisms to build and maintain their shells and skeletons. This is particularly troubling for Alaska’s lucrative shellfish industry. Oysters, clams, and crabs are all feeling the impact, with slower growth rates and increased mortality. The most alarming aspect? Ocean acidification will likely worsen in the coming decades, even as efforts to reduce carbon emissions intensify.
The economic impact of these changes is profound. Alaska’s seafood industry is a powerhouse, contributing $5.8 billion to the economy and employing nearly 60,000 workers. But as fish populations shift and decline, so too do job opportunities and revenues. Communities that depend on a robust fishing industry are feeling the pinch. Fewer fish mean fewer jobs, both directly (harvesters, processors) and indirectly (support services, retail). The ripple effects are vast and far-reaching.
But Alaska is not going down without a fight. Communities, industry leaders, and policymakers are rallying to support the fisheries and the people who depend on them. Some initiatives include:
- Diversifying fishing opportunities to include new species
- Investing in marine research and monitoring
- Promoting sustainable fishing practices
- Supporting education and workforce development to prepare for changing industry needs
The road ahead is uncertain, but one thing is clear: Alaskans are resilient, and they’re committed to preserving their marine heritage for future generations.

Taking Action: Solutions and Innovations
In the face of climatic shifts and environmental challenges, Alaska is pioneering numerous efforts to bolster its resilience and sustainability. One of the key areas of focus is flood prevention. With the increasing threat of melting permafrost and rising sea levels, communities are investing in innovative infrastructure projects. For instance, the construction of seawalls and elevated building structures are becoming more common, aiming to safeguard coastal towns from encroaching waters.
Land stabilization is another critical aspect of Alaska’s combat against environmental challenges. As the permafrost thaws, it leads to unstable land, causing significant issues for infrastructure and ecosystems. To mitigate this, various land stabilization projects are underway. These include the implementation of thermal piles—structures designed to keep the ground frozen—and the use of insulating materials to protect foundations. Additionally, nature-based solutions like revegetation efforts are being employed to stabilize soil and prevent erosion.
Alaska’s fisheries, a cornerstone of the state’s economy and culture, are also under threat from climate change. To ensure their longevity, sustainable management plans are being developed and implemented. These plans include:
- Quota systems to prevent overfishing
- Marine protected areas to preserve biodiversity
- Research initiatives to monitor and understand the impacts of climate change on marine life
By integrating traditional ecological knowledge with modern science, Alaska aims to preserve its fisheries for future generations.
Technology and policy are playing pivotal roles in amplifying these efforts. Tech solutions such as advanced mapping tools and real-time monitoring systems are enhancing the state’s ability to predict and respond to environmental changes. Meanwhile, policies like the Inflation Reduction Act are unlocking significant funds for climate resilience projects, including $2.6 billion allocated for coastal habitat restoration and resilience. This influx of resources is empowering Alaskan communities to fortify their defenses against climatic challenges and build a more sustainable future.
FAQ
What is causing the increased flooding in Alaska?
How are extreme weather events affecting Alaska?
What challenges are Alaska’s fisheries facing?
What steps are being taken to address these issues in Alaska?
- A $100 million plan to prevent future flooding in Juneau.
- Land stabilization projects to combat erosion.
- Sustainable management plans for fisheries.
- Tech solutions like flood-resistant infrastructure and carbon capture.
- Policies like the Inflation Reduction Act to support clean energy projects.
How can individuals contribute to the solution?
- Electrifying their homes.
- Supporting clean energy projects.
- Adopting sustainable practices in their daily lives.
Together, these efforts can make a significant difference in combating climate change.