Welcome to our in-depth exploration of the climatic events of 2024. This article delves into the unprecedented environmental challenges faced globally, highlighting the devastating impact of climate change. From record-breaking heatwaves to catastrophic floods and cyclones, no corner of the Earth was spared. Join us as we uncover the stories behind these events and discuss their lasting implications.
A Global Overview of the Devastating Impact of Climate Change in 2024
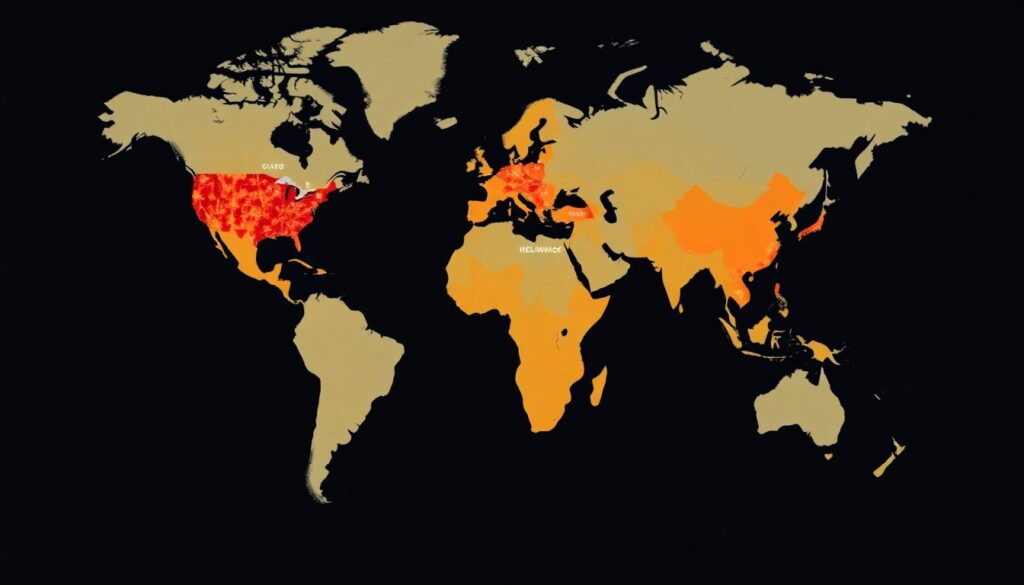
Imagine a global map sprawled out before you, but this is no ordinary atlas. This map is a stark depiction of a world under siege, with a color scheme that screams urgency. Vivid, alarming hues paint the planet, each a cry for help from the Earth itself. Heatwaves are depicted in pulsating reds, sprawling across continents like a feverish rash. Floods engulf low-lying areas in blues so deep they seem to drown the very land beneath them. Cyclones swirl in menacing purples, their tentacles reaching out to wreak havoc.
Look to the tropics, where cyclones spin like mad tops, their paths erratic and unpredictable. Their tendrils stretch out, threatening to engulf everything in their path. Wildfires rage in oranges that burn into your retinas, consuming forests and grasslands alike, leaving behind scorched earth and choking smoke. The colors are stark, almost brutal, a harsh reminder of the reality we face.
This is not a map of the future, but a snapshot of the present. It’s a call to action, a plea from our planet to acknowledge the dire state of affairs. Each color, each disaster, is a testament to the urgent need for change. It’s a map of crisis, yes, but also a map of potential. A potential for us to come together, to take action, and to turn this stark picture into a vision of hope and resilience.

The Heatwave Crisis
The year 2024 will be forever etched in our collective memory as a year of unprecedented heatwaves, shattering records and leaving a trail of devastation in their wake. From North America to Asia, various regions grappled with soaring temperatures that pushed the mercury well beyond historical highs. The impacts were catastrophic, with entire ecosystems thrown into disarray, and communities struggling to cope with the relentless heat.
One of the most heart-wrenching events was the tragedy that unfolded during the Hajj pilgrimage. Thousands of devout Muslims flock to Mecca each year, but the scorching temperatures of 2024 made the journey perilous. The heatwave claimed the lives of many pilgrims, turning what should have been a spiritual journey into a devastating ordeal. The holy city was ill-equipped to handle such extreme weather, leading to a somber and reflective atmosphere among the global Muslim community.
In Europe, the heatwave forced the closure of iconic historical sites. The Acropolis in Athens, a symbol of ancient civilization, was temporarily shuttered as temperatures soared to unsafe levels. Tourists and locals alike were urged to stay indoors, leading to a surreal silence in usually bustling cities. The closure highlighted the vulnerability of cultural heritage sites to extreme weather events, raising concerns about preservation in an era of climate change.
Meanwhile, Mexico and Pakistan faced their own battles against the heat. Both countries recorded temperatures that surpassed all previous records, leading to widespread power outages and water shortages. The impact on wildlife was particularly stark:
- In Mexico, mass die-offs of marine life were reported as ocean temperatures rose.
- In Pakistan, the heatwave decimated populations of native birds and animals, unable to cope with the extreme conditions.

Floods and Deluges
In recent years, devastating floods have swept across the globe, from the desert landscapes of the United Arab Emirates to the lush terrains of Kenya and the historic cities of Europe. These events have left a trail of destruction, disrupting lives and livelihoods, and reminding us of nature’s formidable power.
The impact of these floods has been immense and far-reaching. Infrastructure has been dealt a severe blow, with roads, bridges, and homes damaged or destroyed. In the UAE, streets were turned into rivers, while in Kenya, entire villages were submerged. In Europe, historic sites and vital infrastructure fell victim to the deluge. Among the most affected sectors was agriculture, with croplands washed away and livestock lost.
- Transportation networks have been disrupted, hindering the movement of people and goods.
- Economic losses have been substantial, with businesses and industries facing prolonged closures.
- The emotional toll on individuals and communities has been immense, with many left displaced or living in temporary shelters.
The human cost has been tragic, with loss of life and injuries reported in all affected regions. In Kenya, landslides and flash floods have claimed lives and left families devastated. In Europe, the death toll has been equally alarming, with floods sweeping through populated areas and catching residents off guard. The mental health impact on survivors is an underreported but critical aspect of these events.
Scientists have long warned about the role of climate change in exacerbating these weather events. Rising global temperatures are leading to more frequent and intense rainfall, which overwhelms drainage systems and causes rivers to burst their banks. In the UAE, for instance, a year’s worth of rain fell in just a few days, a pattern that is becoming increasingly common. To mitigate these impacts, global efforts must focus on reducing carbon emissions and investing in resilient infrastructure. Governments and communities worldwide need to prioritize climate adaptation and support vulnerable populations to cope with these challenges.

Cyclones and Hurricanes
The year 2024 witnessed a series of devastating cyclones and hurricanes that left an indelible mark on various regions across the globe. Among the most notable were Hurricane Clara, which originated in the Atlantic and wreaked havoc across the Caribbean and the Eastern Seaboard of the United States, and Typhoon Mangkhut, which ravaged the Philippines and neighboring islands.
Hurricane Clara, a Category 5 storm, carved a path of destruction through the Caribbean. The storm’s ferocious winds and torrential rains caused widespread flooding and infrastructure damage. Islands such as Puerto Rico, the Dominican Republic, and the Bahamas were particularly hard hit. Clara then made landfall in the United States, affecting states from Florida to New York. The economic toll was staggering, with estimates exceeding $50 billion in damages. The human toll was equally devastating, with hundreds of lives lost and thousands displaced.
Meanwhile, in the Pacific, Typhoon Mangkhut brought unprecedented destruction to the Philippines. With sustained winds of over 180 mph, Mangkhut caused catastrophic damage to homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure. The economic impact was severe, with losses estimated at over $20 billion. The humanitarian crisis was equally dire, with thousands of people missing or confirmed dead, and millions left homeless.
Another notable storm was Cyclone Batsirai, which struck the small French island of Mayotte in the Indian Ocean. Although smaller in scale compared to Clara and Mangkhut, Batsirai’s impact was no less devastating for the local population. The cyclone caused extensive damage to the island’s infrastructure, leading to a significant economic setback. The human toll included several fatalities and numerous injuries, with a substantial portion of the population left without shelter or basic amenities. The storm highlighted the vulnerability of small island nations to extreme weather events, underscoring the need for enhanced preparedness and resilience measures.

Droughts and Wildfires
In recent years, severe droughts and wildfires have ravaged the Americas and other regions, leaving devastating impacts in their wake. These extreme weather events, exacerbated by climate change, have transformed vast landscapes into tinderboxes, sparking some of the most destructive wildfires on record. From the Amazon rainforest to the California coast, these fires have engulfed millions of acres, obliterating forests, grasslands, and even entire towns. The sheer scale of these fires has led to unprecedented levels of air pollution, posing significant health risks to local populations. Additionally, the carbon emissions released from these fires contribute to the very climate change that intensifies them, creating a vicious cycle that’s increasingly difficult to break.
The impact on agriculture has been nothing short of catastrophic. Droughts have turned once-fertile lands into dust bowls, making it impossible for farmers to grow crops or raise livestock. The 2019-2020 Australian bushfires, for instance, scorched more than 17 million hectares of land, killing over a billion animals and causing AUD 100 billion in damage, with the agricultural sector bearing the brunt of the losses. In California, the 2020 wildfires destroyed vineyards and orchards, while the 2014-2015 drought cost the state’s agriculture industry an estimated USD 2.7 billion. The loss of agricultural land and resources threatens food security, driving up food prices and leaving vulnerable populations at risk of malnutrition and starvation.
Wildlife has also suffered immensely. The Australian bushfires led to the largest loss of wildlife in the country’s history, with some species being pushed to the brink of extinction. In the Amazon, wildfires have decimated habitats, killing countless animals and leaving survivors to face food and water scarcity. The smoke from these fires can also travel thousands of miles, affecting air quality and wildlife far from the original burn site. Furthermore, the loss of biodiversity has long-term impacts on ecosystems, disrupting food chains and hindering ecosystem services like pollination and water purification.
The long-term effects on food security are perhaps the most concerning. As droughts and wildfires become more frequent and severe, the risk of crop failures and livestock losses increases. This can lead to:
- Reduced food availability,
- Increased food prices,
- Greater dependency on food imports, and
- Increased vulnerability to food shocks.
In turn, these factors can exacerbate malnutrition and hunger, particularly in low-income countries and communities already grappling with food insecurity. To mitigate these risks, it’s crucial to invest in climate-resilient agriculture, early warning systems, and disaster preparedness. Moreover, addressing the root cause of these extremes – climate change – is essential for securing our food future.
FAQ
What were the most significant climate disasters of 2024?
How did climate change influence these disasters?
- Increasing atmospheric and ocean temperatures, fueling extreme weather.
- Altering rainfall patterns, leading to both heavier rainfall and more severe droughts.
- Warming ocean surfaces, which energize tropical cyclones.
What was the economic impact of these disasters?
How did these disasters affect human populations?
What steps can be taken to mitigate future climate disasters?
- Reduce greenhouse gas emissions by transitioning to renewable energy.
- Implement sustainable agricultural practices.
- Improve disaster preparedness and response systems.
- Invest in climate-resilient infrastructure.