Welcome to our comprehensive review of the extreme weather events that shaped 2024. From record-breaking hurricanes to unprecedented droughts and wildfires, this year has been a rollercoaster of climatic extremes. Join us as we explore the most impactful weather events across the globe, and delve into the stories behind the headlines.
A year of storms, wildfires, droughts, and record temperatures
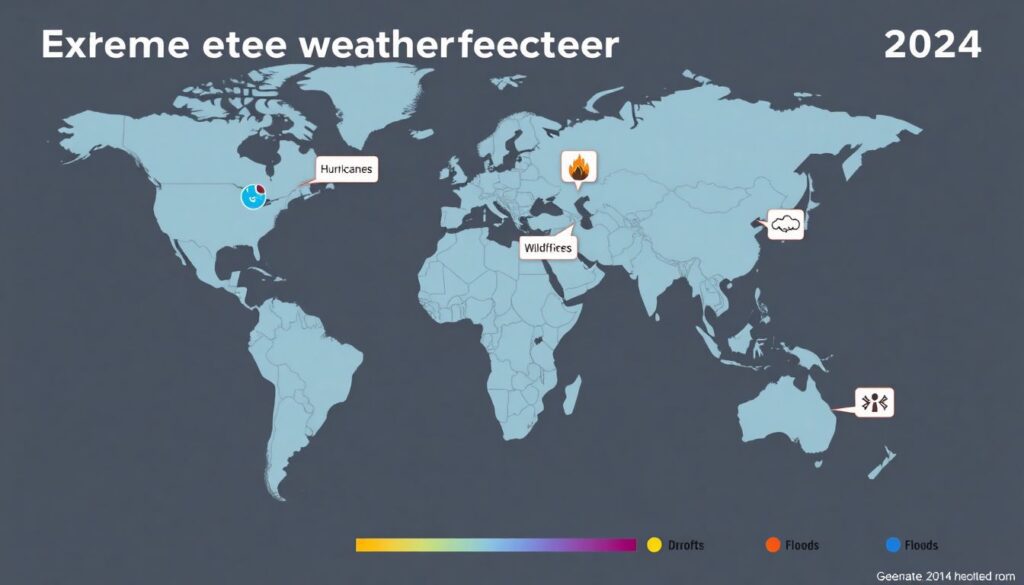
Imagine a global map, vivid and interactive, that serves as a stark reminder of the power and unpredictability of our planet’s climate. This isn’t your ordinary atlas; it’s a living, breathing testament to the events that have shaped our world in 2024. From the swirling maelstroms of hurricanes, represented by ominous twisting icons, to the raging infernos of wildfires, depicted by stark, flickering flames, this map tells a story that is as captivating as it is concerning.
Now, glance across the continents, where parched regions are highlighted in a dusty, sun-scorched hue, signifying the grip of relentless droughts. These areas are not merely geographical locations; they are homes, habitats, and livelihoods, all hanging in the balance. Meanwhile, flood-affected zones are marked by cascading waves, a stark contrast to the arid expanses, but equally devastating in their impact.
As you zoom out, the map reveals a planet in flux, a delicate web of ecosystems responding to the ever-changing climate. Each icon, each color, each highlighted area is more than just data; it’s a call to action, a reminder that we are all connected, and that our future depends on our ability to understand, adapt, and mitigate these extreme weather events.

North America: A Season of Storms
The 2024 Atlantic hurricane season shattered records, leaving an indelible mark on the United States. With an astonishing 25 named storms, it became the third-most active season on record, surpassed only by the 2020 and 2005 seasons. The season was not just notable for its frequency, but also for its intensity, with storms like Beryl, Helene, and Milton leaving a trail of destruction in their wake.
Hurricane Beryl, the second named storm of the season, made landfall in the Carolinas in early June, far earlier than the typical peak of hurricane season. Beryl brought with it torrential rainfall and powerful winds, causing widespread flooding and power outages. The storm resulted in over $3 billion in damages and unfortunately claimed 15 lives. Meanwhile, Hurricane Helene took aim at the Gulf Coast, making landfall as a Category 4 storm. Helene’s catastrophic 140 mph winds and storm surge left a trail of devastation across coastal communities, with damages estimated to be over $10 billion.
Hurricane Milton, the most powerful storm of the season, reached Category 5 status with sustained winds of over 160 mph. Milton’s impact was cataclysmic, causing extensive damage to infrastructure and homes. The storm’s slow movement exacerbated the destruction, with some areas experiencing prolonged, relentless conditions. The combined effects of these storms overwhelmed emergency services, led to massive evacuations, and disrupted daily life for millions of Americans.
As if the hurricane season wasn’t enough, the United States also witnessed unprecedented weather events in other forms. In a stark contrast to the tropical storms, New York State experienced record-breaking snowfall. The sheer volume of snow, reaching up to 100 inches in some areas, paralyzed communities and challenged emergency responders. The extreme weather conditions highlighted the increasing unpredictability of weather patterns and the need for better preparedness and infrastructure to cope with such events. The back-to-back impact of these natural disasters underscored the urgency of addressing climate change and building resilience against future extreme weather events.

South America: Between Floods and Droughts
In the heart of South America, Brazil has been grappling with a duality of natural disasters that have left the country reeling. In the southern state of Rio Grande do Sul, severe flooding and mudslides have transformed the landscape into a scene of devastation. Torrential downpours have caused rivers to burst their banks, submerging entire communities and leaving thousands displaced. The sheer volume of water has led to catastrophic mudslides, sweeping away homes, infrastructure, and livelihoods in their path.
Meanwhile, the central and northeastern regions of Brazil are experiencing the country’s worst drought on record. The usually verdant landscapes have been reduced to parched earth, as reservoirs dry up and crops wither. This environmental crisis has not only affected the agricultural sector but has also led to widespread water shortages, impacting both urban and rural populations. The drought has been so severe that it has even caused blackouts, as hydroelectric power plants struggle to operate without adequate water supplies.
Adding to Brazil’s environmental woes, the Amazon rainforest has been battling record-breaking wildfires. Deforestation and climate change have created a tinderbox of conditions, leading to uncontrollable blazes that have consumed vast swathes of the world’s largest rainforest. The fires have not only destroyed vital habitats and released massive amounts of carbon into the atmosphere, but they have also threatened the lives and cultures of the indigenous communities who call the Amazon home.
In a twist of fate, the eventual arrival of rain in the Amazon has offered a glimmer of hope. The downpours have helped to
- dampen the raging fires, providing some respite for the beleaguered rainforest
- replenish water supplies in drought-stricken regions
- offer a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of Brazil’s ecosystems
. However, the battle is far from over. As the country continues to grapple with these extreme weather events, the need for sustainable environmental policies and climate action has never been more urgent.

Europe: A Tale of Heatwaves and Floods
This summer, Europe is sweltering under a relentless heatwave that has seen temperatures soar higher than average. From the bustling cities of Germany to the picturesque villages of Italy, the mercury has been relentlessly rising, breaking records and causing discomfort for millions. The usually temperate countries like France and the UK have seen temperatures climb above 40°C for the first time in history, turning lush green landscapes into parched, sun-scorched vistas. The intense heat has not only made daily life challenging but also posed significant health risks, especially for the elderly and vulnerable.
In Portugal, the scorching temperatures have fueled an outbreak of devastating wildfires that have consumed vast areas of forest and forced mass evacuations. The country has witnessed some of the most horrific blazes in its history, with flames fanned by strong winds and tinder-dry conditions. The wildfires have not only razed thousands of hectares of land but also claimed lives, destroyed homes, and disrupted livelihoods. Firefighters have been battling day and night to control the infernos, with resources stretched thin by the sheer scale of the disaster.
Meanwhile, Spain has been grappling with a weather phenomenon known as a Depresión Aislada en Niveles Altos (DANA), which has brought catastrophic flooding to parts of the country. The DANA event, characterized by a cold upper-level low pressure system, has caused torrential downpours that have inundated streets, swept away cars, and forced the closure of schools and businesses. Some of the worst-hit regions include:
- Valencia
- Murcia
- Andalusia
The floods have resulted in significant damage to infrastructure, agricultural losses, and sadly, loss of life. Rescue teams have been working tirelessly to evacuate residents from affected areas, as the country comes to terms with the immense destruction caused by this extreme weather event.
The confluence of these extreme weather conditions—from the blistering heatwave to the raging wildfires and catastrophic floods—serves as a stark reminder of the challenges posed by climate change. Scientists warn that such events are likely to become more frequent and severe as global temperatures continue to rise. These weather extremes underscore the urgent need for concerted global action to mitigate climate change and build resilience against its impacts.

Africa and the Middle East: From Droughts to Deluges
In the heart of the Middle East, the United Arab Emirates has been battling intense storms that have brought a rare spectacle to the desert landscape. These storms, often accompanied by thunder and lightning, have led to flash floods and disrupted daily life. With rainfall amounts exceeding annual averages in just a few days, the storms have drawn attention to the impacts of climate change, highlighting the need for improved infrastructure and preparedness.
Meanwhile, West Africa has been grappling with a deadly heatwave that has pushed temperatures to record highs. The scorching heat has led to widespread discomfort and health issues, with countries like Niger and Mali particularly affected. As the mercury continues to rise, communities are struggling to cope, and the heatwave has raised serious concerns about the future of the region’s climate and the well-being of its people.
In contrast, Namibia is experiencing a severe drought that has left much of the country parched. The lack of rainfall has devastated crops and led to water shortages, putting a strain on both farmers and urban residents. As the drought persists, wildlife and livestock are also suffering, with reports of animals dying from thirst. The situation has reached critical levels, prompting calls for international aid and support.
In a surprising turn of events, the Sahara Desert has witnessed unusual flooding in recent months. This vast expanse of sand has seen torrential rains that have transformed dry landscapes into temporary lakes. While the flooding has brought some relief to drought-stricken areas, it has also caused significant damage to infrastructure and disrupted local communities. The unusual weather patterns have left scientists puzzled and underscored the unpredictable nature of our changing climate. Some of the impacts of this flooding include:
- Damage to roads and bridges, isolating communities
- Destruction of homes and displacement of families
- Disruption of agricultural activities and loss of crops
FAQ
What was the most significant hurricane of the 2024 Atlantic hurricane season?
How did the drought in Brazil affect the country?
What caused the catastrophic flooding in Spain?
What were the effects of the heatwave in India?
What steps were taken to address the drought in Namibia?
- Namibia declared a state of emergency in May.
- The government planned to kill wild animals and distribute the meat to those people who had no food.
- The drought was part of a broader El Niño-driven crisis across southern Africa.