Buckle up as we navigate through the tumultuous journey of Boeing in 2024. This isn’t just about a corporate giant facing challenges; it’s a story of resilience, setbacks, and the quest for redemption in the face of adversity. Join us as we explore the recent jet crash disaster in South Korea, its impact on Boeing, and the company’s ongoing efforts to restore its shine.
A Look into Boeing’s Turbulent Year and Its Path to Recovery
Imagine a Boeing 737-800, once a symbol of technological prowess, now cutting through the sky in distress, a thick plume of black smoke billowing from its engine. The plane’s shiny fuselage, emblazoned with the company’s iconic livery, is now a stark contrast against the ominous backdrop of Boeing’s sprawling headquarters in Chicago.
The corporate campus, usually a hub of innovation and progress, now stands as a silent witness to the unfolding drama. The building’s reflective surfaces mirror the distress in the sky, as the plane’s erratic path is mimicked by the tumultuous lines of a stock market graph displayed on a giant screen behind the headquarters.
The graph, a stark representation of Boeing’s fortunes, shows a steep decline, each drop a echo of the plane’s descent. The once steadily climbing line, a testament to Boeing’s historic success, is now a cascading waterfall of red, reflecting the market’s real-time response to the crisis unfolding in the sky.
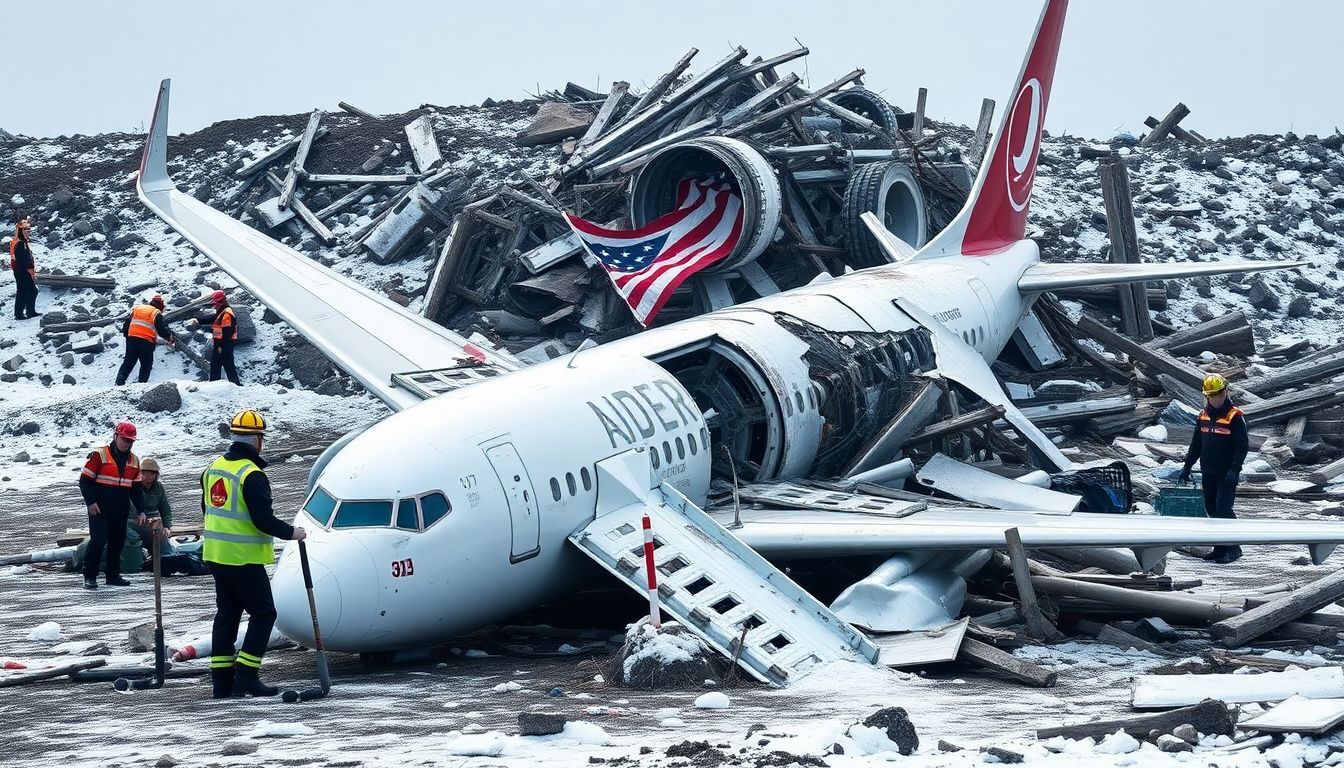

A Fateful Day in South Korea
In the quiet skies over South Korea, a sudden tragedy struck as a Boeing 737-800 jetliner, operated by a local low-cost carrier, plummeted to the ground. The eerie silence that followed the deafening crash served as a harsh reminder of the human impact of such events. On board were 82 souls, each with their own stories, dreams, and loved ones waiting for their safe return. The impact was catastrophic, leaving no survivors, and sending shockwaves through the tight-knit local community and the global aviation world.
The initial responses from Boeing and aviation experts were swift. Boeing, the manufacturer of the ill-fated jet, expressed their condolences to the families of the victims and pledged their full cooperation with the investigation. Aviation experts, on the other hand, were quick to point out the differences between the 737-800 and the controversial 737 Max models. The 737-800, a staple of many airlines’ fleets, has a proven safety record, unlike the 737 Max, which was grounded worldwide following two fatal crashes in 2018 and 2019. Here are some key differences:
- The 737-800 is part of the 737 Next Generation (NG) series, while the 737 Max is a newer, re-engined version.
- The 737 Max features larger, more fuel-efficient engines and aerodynamic improvements, while the 737-800 does not.
- The 737 Max has a problematic flight control system, the Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System (MCAS), which was not present on the 737-800.
As the investigation unfolds, the world watches and waits for answers. The human impact of this tragedy is immeasurable, serving as a grim reminder of the importance of air safety. The differences between the 737-800 and the 737 Max, though significant, do not diminish the urgency for a thorough investigation. Every life lost deserves justice, and the aviation industry owes it to them to learn from this tragedy and make the skies safer for all.
Boeing’s Troubled Timeline
Boeing, once a symbol of American innovation and industrial might, has faced a series of challenges that have left the aerospace giant grappling for stability. The year 2024 has been particularly tumultuous, with issues ranging from labor disputes to quality control problems and financial setbacks. At the forefront of these challenges is the machinists’ strike, which has brought production lines to a halt. The strike, a result of stalled contract negotiations, has highlighted the growing tension between management and labor, a rift that has been widening since the 737 Max crashes of 2018 and 2019.
In the midst of the strike, Boeing was dealt another blow with the ‘door plug incident‘. This quality control issue, where door plugs were left inside fuel tanks, grounded dozens of 737 Max planes. This incident is a stark reminder of the systemic issues that have plagued Boeing since the 737 Max crashes. It raises questions about the company’s quality control processes and the cultural shifts promised in the wake of the tragedies. The incident has also drawn scrutiny from regulators, further complicating Boeing’s path to recovery.
The repercussions of these events have been starkly reflected in Boeing’s stock price decline. Investors, wary of the ongoing issues and the company’s seemingly endless crisis mode, have been selling off their shares. Here’s a breakdown of the stock price decline:
- Early 2024: Boeing shares were trading at around $200.
- Post-strike announcement: Shares fell by about 10%.
- Post-door plug incident: Shares experienced another significant drop, bringing the total decline to over 20% since the start of the year.
To understand Boeing’s struggles in 2024, it’s crucial to look at the broader context of the company’s trials since the 737 Max crashes. The crashes, which claimed 346 lives, were a catastrophic failure of both technology and oversight. They led to the grounding of all 737 Max planes worldwide, costing Boeing billions in losses. The crashes also revealed deep-seated issues within Boeing’s corporate culture, leading to the departure of then-CEO Dennis Muilenburg. Since then, Boeing has been navigating a complex web of legal battles, regulatory scrutiny, and public relations crises. The challenges of 2024 are not isolated incidents, but rather, echoes of this ongoing saga.

The 737 Max Saga
The 737 Max crashes in 2018 and 2019 sent shockwaves through the aviation industry, leaving 346 people dead and raising critical questions about aircraft safety and corporate responsibility. On October 29, 2018, Lion Air Flight 610 crashed into the Java Sea shortly after takeoff. Less than five months later, on March 10, 2019, Ethiopian Airlines Flight 302 met a similar fate, crashing near Bishoftu. Both accidents involved the new Boeing 737 Max aircraft and occurred due to a faulty flight control system called MCAS (Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System).
The subsequent investigations revealed a disturbing pattern of corporate negligence and regulatory oversight failure. Key findings included:
- Boeing’s design and certification process for the 737 Max was flawed, with the company concealing crucial information about MCAS from pilots and regulators.
- The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) delegated substantial certification responsibilities to Boeing, leading to a lack of adequate oversight.
- Boeing employees faced significant pressure to prioritize cost-cutting and expedite the 737 Max’s certification process.
The investigations’ results severely impacted Boeing’s reputation and finances. Boeing’s once-sterling reputation for safety and quality was tarnished, leading to a loss of trust among regulators, airlines, and the public. The financial ramifications were equally severe, with the company reporting a $636 million loss in 2019 – its first annual loss in over two decades. The 737 Max grounding, which lasted from March 2019 to November 2020, cost Boeing an estimated $20 billion.
In January 2021, Boeing agreed to pay over $2.5 billion in fines and compensation as part of a deferred prosecution agreement with the U.S. Department of Justice, admitting to criminal misconduct. However, in a surprising turn of events, U.S. District Judge Reed O’Connor rejected the deal in February 2023, stating that the agreement was not in the public’s best interest. Judge O’Connor cited the need for greater transparency and accountability, noting that the deal did not adequately address the corporate culture that led to the 737 Max crashes. This recent development has left Boeing’s path forward uncertain, with potential further legal and financial repercussions looming.

Boeing’s Path to Redemption
In the wake of the 737 MAX crisis, Boeing has been steadfast in its efforts to transform its corporate culture and prioritize safety. The aerospace giant has implemented several initiatives, including company-wide safety meetings, to ensure that every employee understands the importance of safety in their daily tasks. One of the most significant changes was the departure of CEO Dennis Muilenburg, replaced by David Calhoun in January 2020. Calhoun inherited a company in crisis and was tasked with steering Boeing through one of the most challenging periods in its history.
Calhoun’s tenure saw significant steps towards improving safety and rebuilding trust. He oversaw the establishment of a new safety organization, charged with reviewing all aspects of safety management and reinforcing a culture of transparency and accountability. However, Calhoun’s departure in March 2023 has left the company at a critical juncture. His successor will need to continue these efforts and continue to drive cultural change.
Looking ahead, Boeing faces several challenges and opportunities:
-
Regulatory Compliance:
Boeing must continue to work closely with regulators such as the FAA to ensure that its aircraft meet the highest safety standards.
-
Supply Chain Management:
The company needs to navigate ongoing supply chain disruptions and ensure the timely delivery of parts and components.
-
Innovation:
Boeing has the opportunity to invest in new technologies and sustainable aviation solutions, positioning itself as a leader in the future of flight.
The path forward for Boeing is not without obstacles, but the company has a unique opportunity to reinvent itself. By continuing to prioritize safety, innovation, and cultural transformation, Boeing can reclaim its position as a trusted and respected leader in the aerospace industry. The coming years will be crucial in determining Boeing’s future, and the world will be watching closely as the company writes its next chapter.
FAQ
What is the difference between the Boeing 737-800 and the 737 Max?
How have Boeing’s troubles affected its competition with Airbus?
What were the results of Boeing’s guilty plea?
What steps has Boeing taken to improve safety?
- Hosted company-wide safety meetings involving 70,000 employees.
- Introduced more intensive training programs.
- Implemented stricter manufacturing safety protocols.