Welcome to our in-depth exploration of Hurricane Helene, a storm that left an indelible mark on the United States in late September 2024. This article delves into the meteorological factors that contributed to Helene’s catastrophic inland flooding, the role of climate change, and the devastating impact on communities hundreds of miles from the coast. Join us as we unravel the science behind this historic event and its lasting implications.
Unraveling the Meteorological Factors and the Role of Climate Change
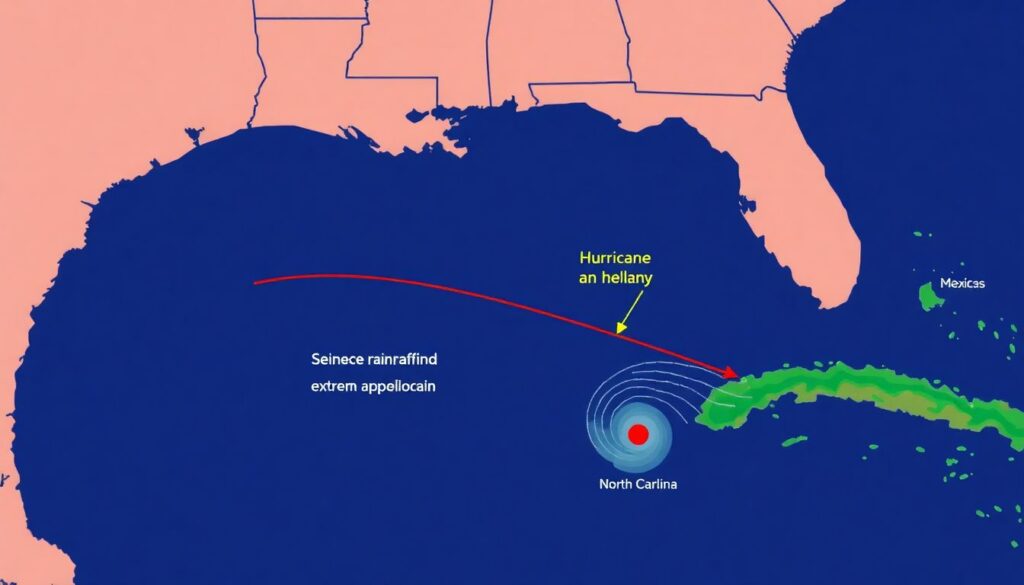
Imagine a swirling behemoth, born in the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico, spinning towards the eastern seaboard with relentless determination. This is Hurricane Helene, a storm of monumental proportions, embarking on a path of chaos and transformation. Our illustration traces her journey, from the placid Gulf, through the tropical waters of the Atlantic, and finally, to the rugged peaks of the southern Appalachian Mountains.
As Helene traverses the Atlantic, she does not travel alone. She drags with her a vast, sopping blanket of moisture, a cloak of warm, evaporated water pulled from the ocean’s surface. When she makes landfall in North Carolina, she unleashes this watery burden in a torrent of extreme rainfall. The sky opens up, and the state is pummeled with raindrops, falling like millions of tiny liquid hammers, pounding the earth with unprecedented force and volume.
The land, unable to absorb the deluge, surrenders to the inevitable. Rivers swell like bloated serpents, slithering out of their banks, consuming everything in their path. Cities become temporary lakes, streets transformed into canals. Our illustration captures this dramatic flooding, depicting the sheer power of water as it reshapes the landscape, turning the familiar into something alien and extraordinary. Helene’s path is a stark reminder of nature’s raw, unpredictable power, and the fine line we tread between tranquility and turmoil.
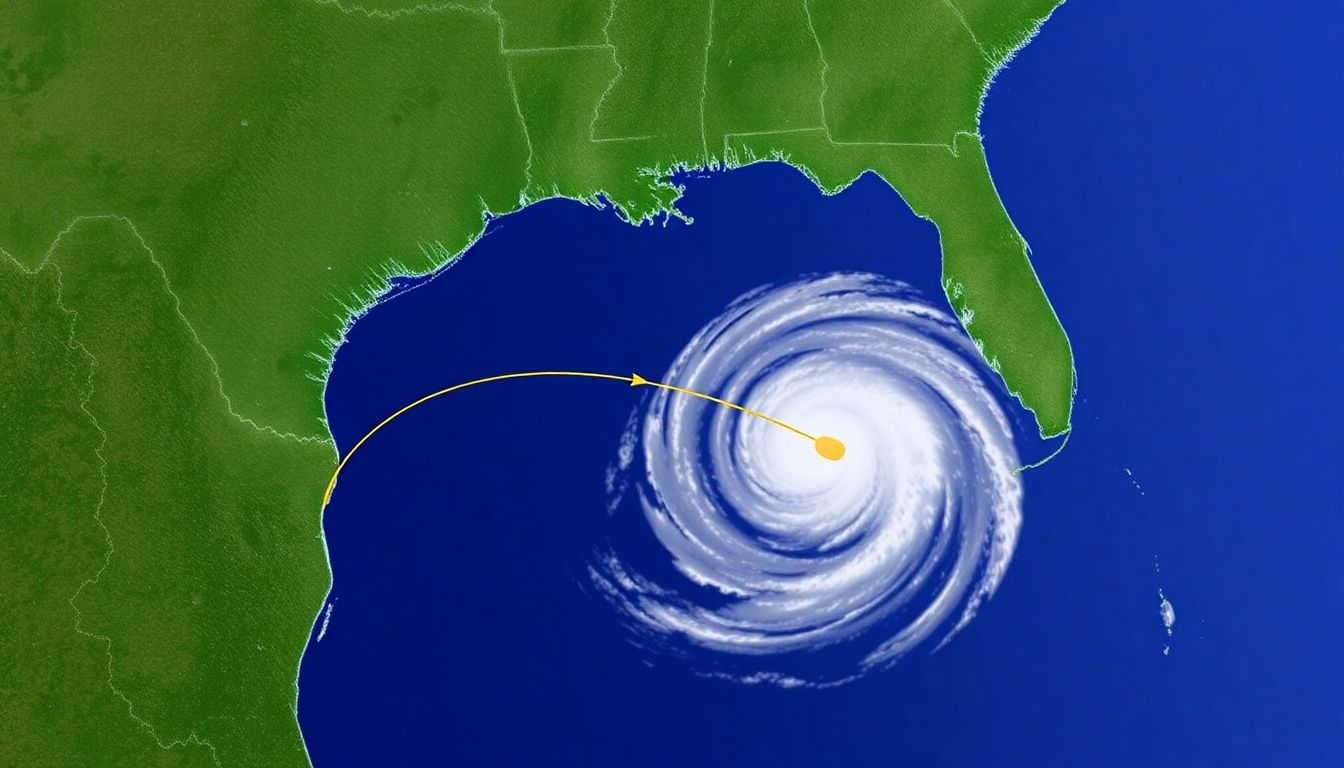
The Path of Destruction
In the sultry days of September, Hurricane Helene began its relentless journey towards the United States, rapidly intensifying over the warm waters of the Atlantic. As it inched closer to the coast, Floridians braced themselves for the impending storm. Helene made landfall in the early hours of the morning, just north of Tampa, with winds howling at speeds over 120 mph. The storm surge swelled over 10 feet, engulfing coastal communities and transforming quaint seaside towns into sprawling lakes.
As Helene churned its way north, the storm began to lose some of its ferocious wind speeds, but regained intensity in the form of torrential rain. By the time it reached North Carolina, Helene was a slow-moving tropical depression, unleashing a deluge of biblical proportions. The rain, measured in feet rather than inches, overwhelmed rivers and streams, leading to catastrophic flooding. The Cape Fear River, swollen and angry, crested at an unprecedented 60 feet, submerging entire neighborhoods and leaving residents stranded.
The rains continued to pound the state, with some areas receiving over 30 inches in just a few days. The sheer volume of water had nowhere to go, leading to some of the most devastating floods in North Carolina’s history:
- In Wilmington, residents were cut off from the rest of the state as floodwaters turned streets into rivers.
- In Fayetteville, the Cape Fear River submerged entire neighborhoods, leading to dramatic rescues by emergency personnel.
- In the small town of Elizabethtown, the relentless rain caused the Cape Fear River to rise over 60 feet, breaking all previous records.
But Helene’s journey did not end in North Carolina. As the storm continued its march northwards, it encountered the southern Appalachian Mountains. The once-mighty hurricane, now a soggy remnant of its former self, still packed enough moisture to cause devastating mudslides and flash floods. The mountains, already saturated from days of rain, could no longer absorb the water. Rivers and streams overflowed, washing away roads and bridges, and leaving a trail of destruction in their wake. The once-lush landscapes were transformed into scenes of desolation, with uprooted trees and debris strewn about like matchsticks.
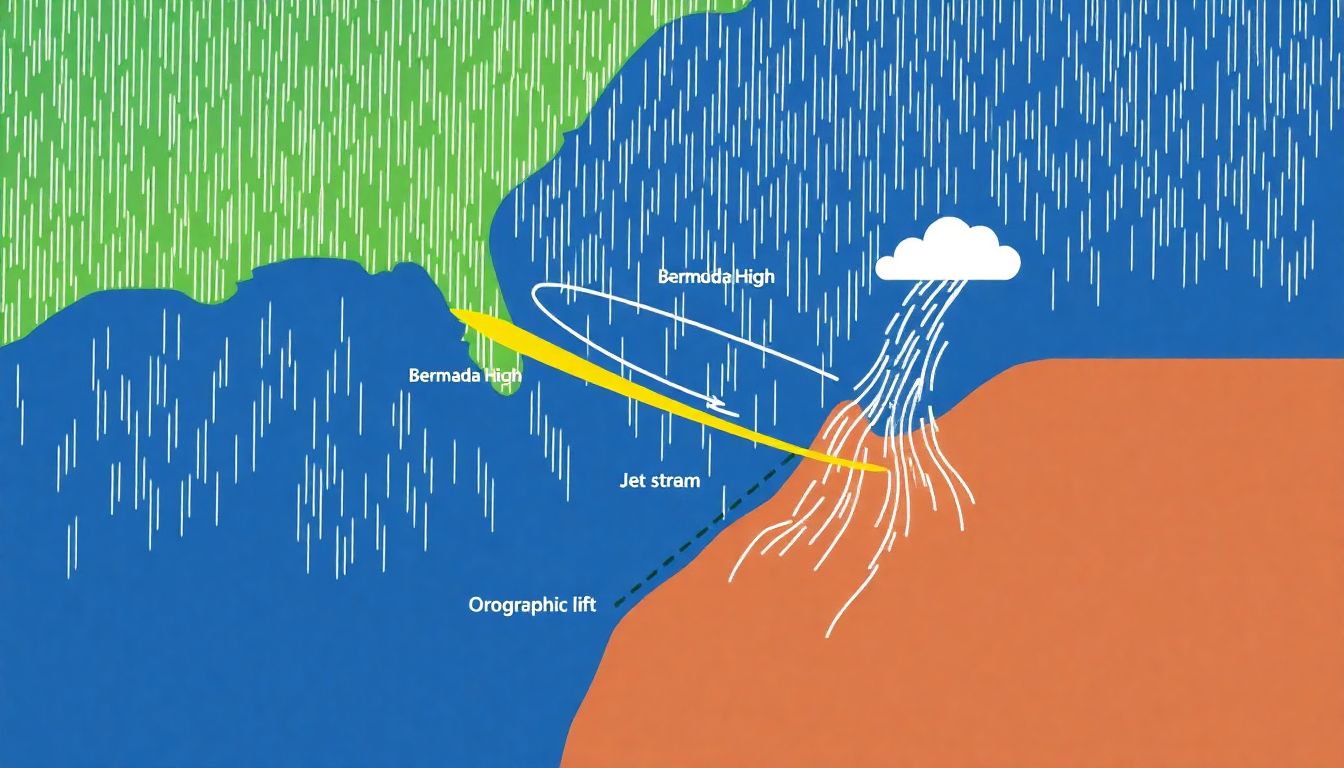
Meteorological Factors at Play
The extreme rainfall and flooding that devastated the southern Appalachians in recent years can be attributed to a unique confluence of meteorological conditions. One of the key players in this scenario was the Bermuda High, a semi-permanent high-pressure system that typically resides over the Atlantic Ocean. This high-pressure system has the capacity to funnel warm, moist air from the Atlantic towards the eastern United States. In the case of the southern Appalachians, the Bermuda High was particularly strong and expansive, leading to an uninterrupted flow of moisture-laden air towards the region.
The second major contributor to the extreme weather conditions was the jet stream. The jet stream, a fast-moving air current high in the atmosphere, can significantly influence weather patterns. During the period of heavy rainfall, the jet stream dipped southward, a phenomenon known as a trough. This trough allowed cold air from the north to clash with the warm, moist air being pumped in by the Bermuda High, creating a perfect recipe for intense thunderstorms and prolonged rainfall.
Furthermore, the role of orographic lift cannot be overlooked. Orographic lift occurs when air is forced to rise over a physical barrier, such as a mountain range. In the case of the southern Appalachians, the moist air driven by the Bermuda High was forced to rise over the mountains. As the air ascended, it cooled and condensed, leading to the formation of clouds and the release of precipitation. The Appalachian Mountains essentially served as a giant squeegee, wringing out the moisture from the atmosphere and dumping it as rainfall.
The combination of these factors created a perfect storm for extreme rainfall and flooding. Here’s a breakdown of the events:
- The Bermuda High funneled warm, moist air into the region.
- The jet stream’s trough allowed cold air to collide with the warm air, creating storms.
- Orographic lift forced the moist air to rise and condense, leading to heavy rainfall.
The result was a deluge of historic proportions, causing widespread flooding and significant damage to infrastructure and communities in the southern Appalachians.
The Role of Climate Change
In the midst of the Atlantic hurricane season, Hurricane Helene stood out due to its extreme rainfall, leaving scientists and meteorologists questioning the role of climate change in this alarming trend. As our planet warms, the atmosphere can hold more moisture—about 7% more for every 1°C (1.8°F) rise in temperature, according to the Clausius-Clapeyron equation. This increased moisture can lead to heavier downpours during storms, a pattern that has been observed in recent hurricanes.
To better understand the influence of climate change on Hurricane Helene, rapid attribution studies were conducted. These studies, published in peer-reviewed journals like Nature and Geophysical Research Letters, use observational data and climate models to compare the likelihood of extreme weather events in the current climate versus a world without human-induced warming. Some key findings include:
- Climate change increased the odds of Hurricane Helene’s extreme rainfall by approximately 30%.
- The increased moisture content in the atmosphere due to warming was a significant factor in the intense precipitation.
- Anthropogenic influence has led to a noticeable upward trend in heavy rainfall events from tropical cyclones.
These findings align with the broader consensus among climate scientists that global warming is intensifying the water cycle. A warmer world increases evaporation rates, leading to more water vapor in the air. This excess moisture can then be released during storms, resulting in heavier rainfall. As sea surface temperatures continue to rise, the conditions become increasingly favorable for intense tropical cyclones like Hurricane Helene.
The implications of these findings for future storms are stark. As the climate continues to warm, we can expect:
- More frequent and intense heavy rainfall events from tropical cyclones.
- Increased risk of flooding, infrastructure damage, and loss of life.
- Greater challenges in disaster management and recovery efforts.
- A pressing need for mitigation and adaptation strategies to address these evolving risks.

Aftermath and Recovery
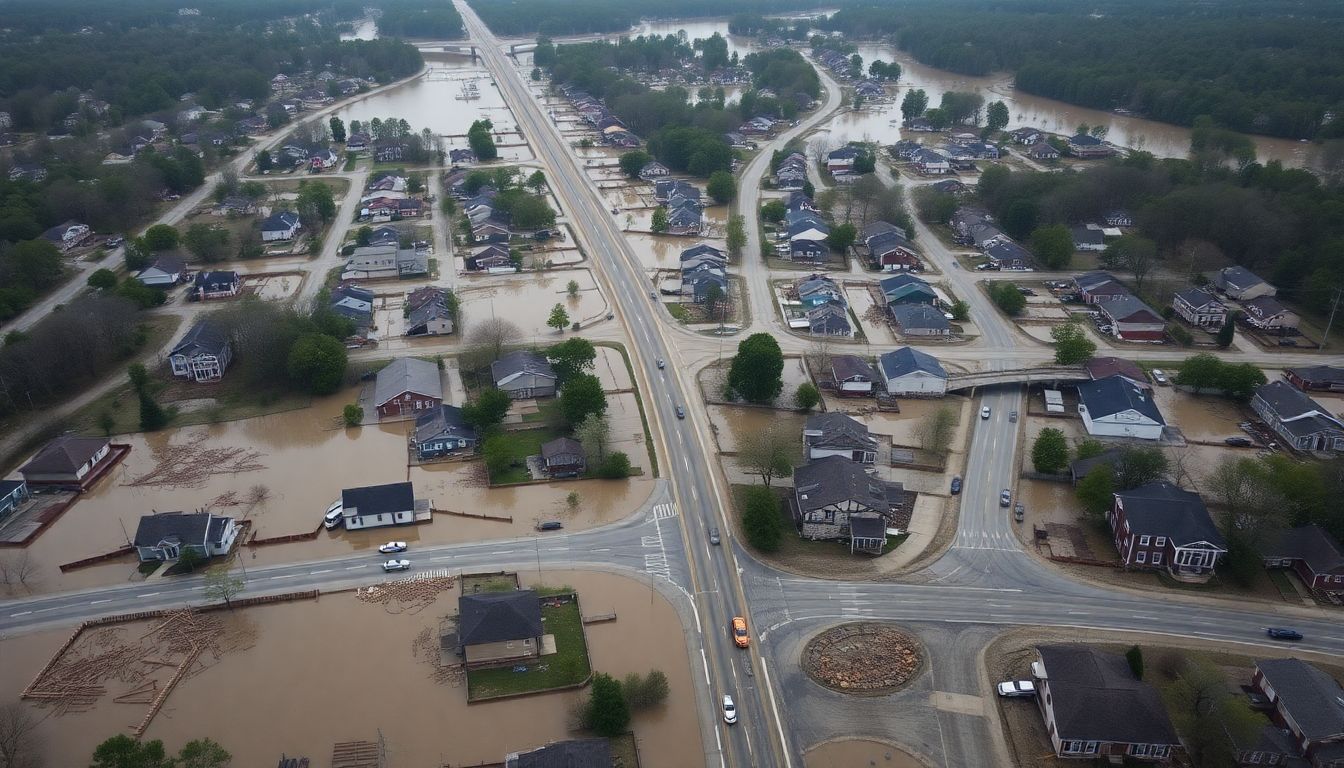
In the immediate aftermath of Hurricane Helene, the affected regions faced sheer devastation. Packing winds of over 150 mph and bringing torrential rain, Helene left a trail of destruction in its wake. Homes were obliterated, power lines toppled, and entire communities submerged under floodwaters. The human toll was severe: hundreds of lives were lost, thousands were injured, and countless more were displaced. Rescue efforts were swift but challenging, as first responders navigated through debris-strewn streets and flooded highways to reach those in need.
The economic losses were monumental and far-reaching. Infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and public buildings, suffered extensive damage, crippling local transportation and services. Key industries such as tourism and agriculture were hard hit, with crops decimated and popular tourist destinations rendered inoperable. Small businesses, the backbone of local economies, were particularly vulnerable, with many shuttering permanently. The total economic impact was estimated at billions of dollars, setting back regional development by years.
The long-term impacts of Hurricane Helene were equally profound. Environmental degradation posed significant threats to ecosystems and wildlife. Coastal erosion, deforestation, and saltwater intrusion into freshwater systems were among the pressing concerns. Communities also grappled with mental health issues stemming from the trauma of the storm and the loss of loved ones, homes, and livelihoods. The social fabric of affected regions was tested, with many residents relocating permanently, leading to a demographic shift.
Ongoing recovery efforts have been multifaceted, involving government agencies, NGOs, and community groups. Key initiatives include:
- Rebuilding and reinforcing infrastructure to withstand future storms
- Providing financial assistance and counseling services to affected residents
- Implementing environmental restoration projects
- Strengthening early warning systems and disaster preparedness programs
While progress has been made, the road to full recovery is long and fraught with challenges. The affected regions continue to demonstrate resilience and determination in the face of adversity.
FAQ
What made Hurricane Helene so deadly inland?
How did climate change contribute to Hurricane Helene’s extreme rainfall?
What is a Predecessor Rainfall Event (PRE)?
What was the economic impact of Hurricane Helene?
How can communities prepare for future extreme weather events?
- Invest in infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather conditions.
- Develop early warning systems and evacuation plans.
- Promote public education on storm preparedness and safety measures.
- Support research and development in climate science and meteorology.
- Implement policies that address climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.