Welcome to this comprehensive overview of Tanzania’s tumultuous year of 2024. This article delves into the natural and man-made disasters that have shaped the country’s recent history, highlighting the urgent need for improved infrastructure, disaster preparedness, and urban planning. Join us as we explore the lessons learned from these challenging events and discuss the path forward to building a more resilient future.
Examining Tanzania’s tumultuous year and the path to resilience
Imagine a sprawling canvas capturing the breadth of Tanzania’s landscapes, from the bustling streets of Dar es Salaam to the serene villages nestled within the shadows of Mount Kilimanjaro. This is not a scene of tranquility, but a stark depiction of a year marked by nature’s fury and unexpected catastrophes. Welcome to 2024, a year that tested the resilience of Tanzania and its people.
Beginning with the torrential downpours that swept through the country in early 2024, our timeline first illustrates the devastating floods that submerged both urban and rural areas. Cars bobbing in water-filled streets of Dodoma, while farmers in Morogoro watch their crops wash away. As the year progresses, so do the disasters. The canvas darkens with the hues of mud and debris, depicting the landslides that ravaged the slopes of the Uluguru Mountains, burying homes and lives beneath them.
Moving through the timeline, the scene shifts to the heart of Tanzania’s cities. Buildings crumble and collapse under the weight of shoddy construction and unexpected tremors, choking the air with dust and despair. Meanwhile, fires blaze in both the urban slums and the rural bushlands, painting the backdrop a fierce orange. The year 2024 becomes a testament to the indomitable spirit of Tanzanians, who time and again, rise from the ashes and rebuild their lives.

The Floods of 2024
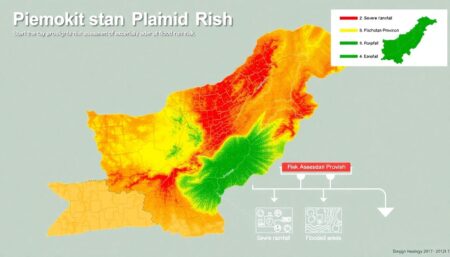
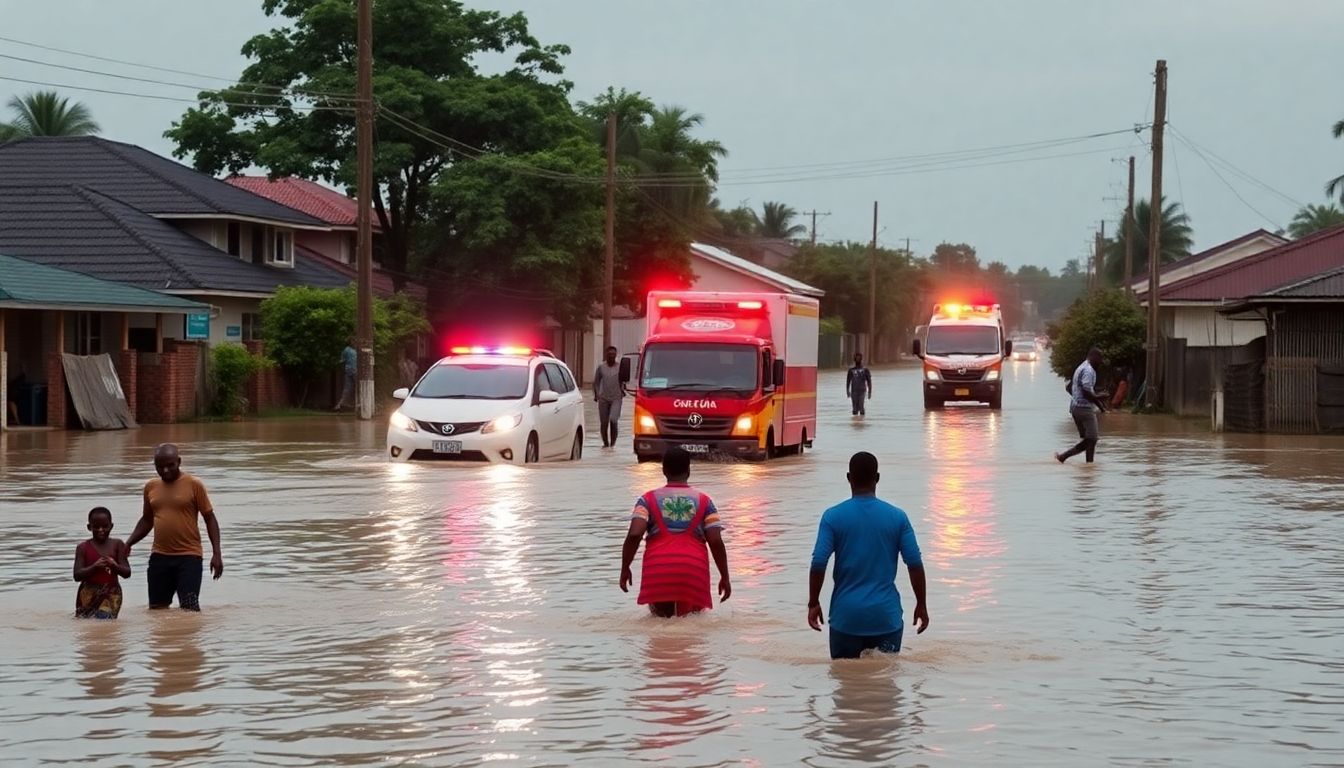
The El Niño weather phenomenon, a periodic climatic event, has had a profound impact on Tanzania, particularly through widespread flooding in both urban and rural areas. This natural occurrence, characterized by unusually warm ocean temperatures in the Equatorial Pacific, has led to heavy rainfall and severe flooding, wreaking havoc on communities and ecosystems alike. The devastation caused by these floods is immense, with loss of life, displacement of families, and significant economic costs topping the list of tragic consequences.
The flooding has left a trail of destruction in its wake. Key infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and buildings have been damaged or completely destroyed, paralyzing transportation and communication networks. Crops have been wiped out, leading to food shortages and increased poverty. The economic costs are staggering, with the Government of Tanzania and international aid agencies allocating millions of dollars towards emergency response and reconstruction efforts. The World Bank estimates that the economic impact of these floods can set back development progress by years, posing a significant threat to Tanzania’s economic growth and stability.
The human toll is equally devastating. Communities have been displaced, with thousands of people forced to leave their homes and seek refuge in temporary shelters. The flooding has also led to a rise in waterborne diseases, putting already vulnerable populations at even greater risk. According to reports from the Tanzania Red Cross Society, the number of lives lost and individuals affected by El Niño-related floods continues to rise with each occurrence, underscoring the urgent need for better preparedness and response mechanisms.
To mitigate the impact of future El Niño events, it is crucial to prioritize better urban planning and the development of flood-resistant infrastructure. This includes:
- Investing in early warning systems to enhance preparedness and response.
- Building and maintaining robust drainage systems to manage excess water.
- Ensuring that new buildings and infrastructure are designed to withstand flooding.
Moreover, there is a need for comprehensive land use planning to prevent settlements in flood-prone areas. By taking these proactive steps, Tanzania can significantly reduce the devastation caused by El Niño and build a more resilient future for its citizens.
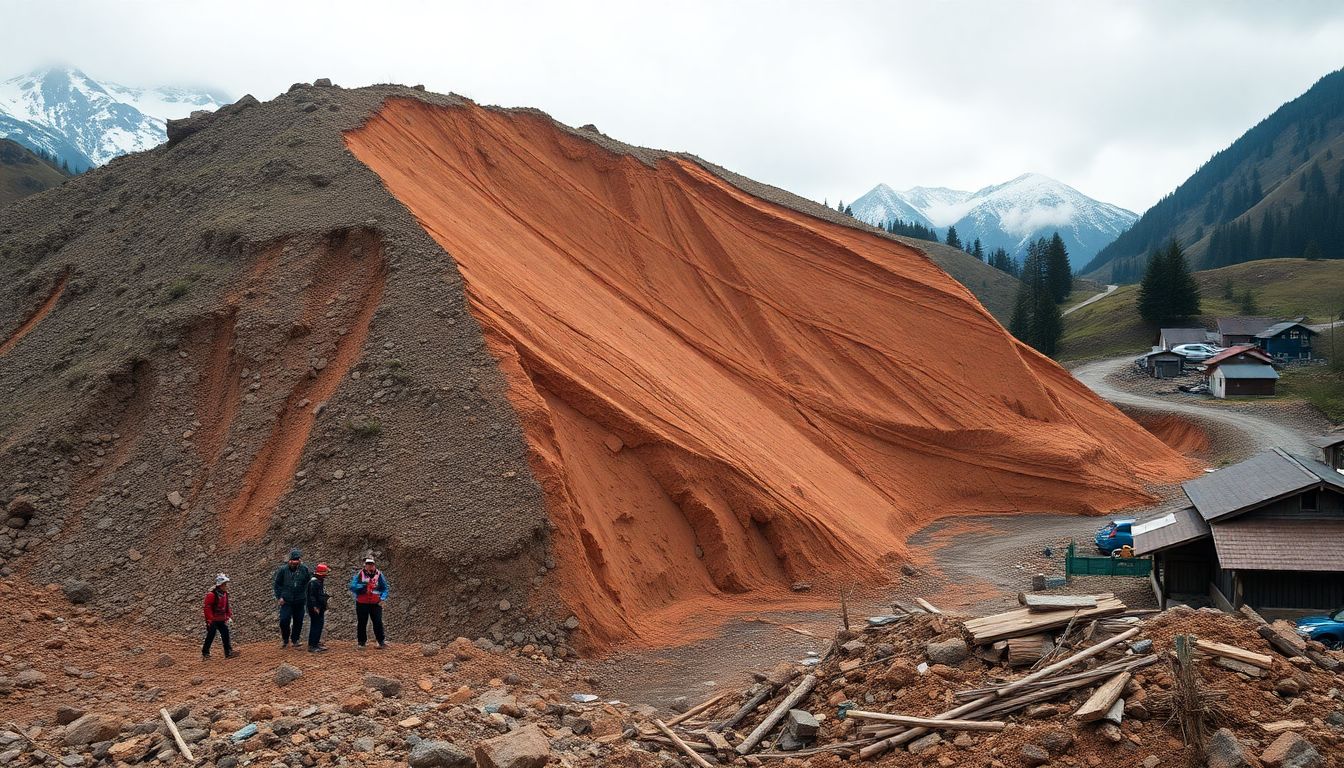

Deadly Landslides
In the heart of Tanzania, the regions of Hanang and Mbeya have recently faced devastating landslides, leaving a trail of destruction and grief in their wake. In Hanang, a massive landslide in 2020 resulted in 15 fatalities and displaced over 500 residents. The economic impact was severe, with crucial infrastructure such as roads and farmlands destroyed, isolating communities and disrupting livelihoods. Meanwhile, Mbeya’s harrowing experience in 2021 saw 19 lives lost and over 1,000 people displaced, with significant damage to homes, businesses, and public utilities, paralyzing local economies.
The catalyst for these tragic events was a combination of heavy rainfall and the regions’ steep terrain. Intense downpours saturated the soil, reducing its stability and causing the ground to give way. The hilly landscapes of Hanang and Mbeya further amplified the risk, as gravity aided the rapid downward movement of earth and debris, creating a powerful and destructive force.
The need for better land-use planning and early warning systems in these regions has never been more apparent. To mitigate the impact of future landslides, several measures can be undertaken, including:
- Implementing proper land-use zoning to restrict settlements in high-risk areas.
- Promoting afforestation and soil conservation techniques to stabilize slopes and reduce soil erosion.
- Establishing community-based early warning systems to ensure timely evacuations.
- Investing in real-time weather monitoring and hydrological systems to enhance preparedness.
By embracing these strategies, Tanzania can significantly reduce the loss of life, displacement, and economic devastation caused by landslides, fostering more resilient communities in Hanang, Mbeya, and beyond.

Urban Disasters: Building Collapses and Fires
In the bustling heart of Dar es Salaam, the district of Kariakoo witnessed a devastating building collapse that sent shockwaves through the community. The incident, which occurred due to poor construction standards, highlighted the grim reality of inadequate building regulations. The collapse not only claimed lives but also left many injured and displaced, raising serious concerns about the integrity of structures in the area.
Concurrently, a series of market fires have plagued Dar es Salaam and Mwanza, causing significant economic losses and endangering lives. The inadequate fire safety measures in these urban markets have exacerbated the situation, turning what could have been contained incidents into full-blown disasters. The fires have not only destroyed livelihoods but also disrupted the local economy, affecting thousands of residents and traders.
Several factors have contributed to these disasters, including:
- Substandard Construction Materials: The use of low-quality materials in construction has compromised the structural integrity of buildings.
- Lack of Building Inspections: Inadequate or infrequent inspections have allowed unsafe structures to go unnoticed.
- Insufficient Fire Safety Protocols: The absence of proper fire safety measures, such as fire extinguishers, sprinkler systems, and clear evacuation routes, has made markets vulnerable to fires.
- Overcrowding: The dense population and congested spaces in urban markets have facilitated the rapid spread of fires.
There is an urgent need for stricter building regulations and improved fire safety in urban markets. Local authorities must enforce rigorous building codes to ensure that structures are safe and resilient. Additionally, implementing comprehensive fire safety measures, including regular inspections, fire drills, and the installation of fire safety equipment, is crucial. Community education on fire prevention and safety protocols can also play a significant role in mitigating future disasters. By addressing these issues proactively, we can create safer and more resilient urban environments for all.

Road Traffic Accidents and Public Health Crises
In recent years, Tanzania has witnessed an alarming rise in road traffic accidents, a issue that has become a significant public safety concern. According to recent reports, the number of fatalities and injuries due to road accidents has been increasing at an unprecedented rate. Several factors contribute to this grim trend. Poor road infrastructure, characterized by potholes, lack of proper signage, and inadequate lighting, plays a significant role in these accidents. Additionally, the absence of strict traffic law enforcement, such as speed limits and drunk driving regulations, further exacerbates the problem. The combination of these elements creates a dangerous environment for drivers, pedestrians, and passengers alike.
Beyond the immediate causes, there are deeper societal issues at play. The rapid increase in vehicle ownership without a corresponding improvement in road quality and maintenance has led to congestion and hazardous driving conditions. Furthermore, limited public transportation options force many residents to rely on unsafe modes of transport, such as overloaded buses and motorcycles. To reverse this worrying trend, comprehensive measures must be taken. These include:
- Investing in better road maintenance to ensure that roads are safe and well-marked.
- Implementing stricter traffic laws and enforcement to deter reckless driving and promote road safety.
- Enhancing public transportation infrastructure to provide safer alternatives to private vehicles.
Concurrently, Tanzania is grappling with a resurgence of cholera outbreaks, a waterborne disease that thrives in conditions of poor sanitation and hygiene. The recurring episodes of cholera point to systemic failures in public health infrastructure. Inadequate access to clean water, lack of proper waste management, and poor sanitation facilities in both urban and rural areas are the primary culprits. To combat this public health crisis, it is imperative to focus on:
- Improving access to clean water through investments in water treatment and distribution systems.
- Enhancing waste management practices to prevent contamination of water sources.
- Promoting public health education to raise awareness about hygiene and sanitation practices.
FAQ
What were the main natural disasters that affected Tanzania in 2024?
What were the primary causes of the man-made disasters in 2024?
How did the floods impact Tanzania’s infrastructure and economy?
- Entire communities were submerged, destroying homes and vital farmlands.
- Transportation routes were disrupted, paralyzing daily life and commerce.
- The financial cost of the floods was estimated at over 150bn/-, pushing many households into financial distress.
What measures can Tanzania take to prevent future landslides?
- Implement better land-use planning and early warning systems.
- Invest in infrastructure development in high-risk areas.
- Promote sustainable agricultural practices to stabilize soil.
How can Tanzania improve urban safety and prevent disasters like building collapses and fires?
- Enforce stricter building regulations and conduct regular safety inspections.
- Improve fire safety measures in markets, including proper electrical installations and firefighting equipment.
- Promote public awareness campaigns on safety standards and emergency preparedness.