In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, one question has been on the minds of tech enthusiasts, data center managers, and investors alike: ‘What’s next for server processing power?’
The answer, it seems, is coming from none other than Intel. The tech giant has been quietly prepping a monster of a server CPU, set to hit the market in 2025. This isn’t just any upgrade; it’s a leap forward that promises to redefine what we expect from our servers.
But why should you, as an investor or a tech enthusiast, care about a CPU that’s still a few years away? The purpose of this article is to shed light on this upcoming powerhouse, explore what it means for the future of computing, and guide you on how to prep your portfolio or knowledge base for this significant shift.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of Intel’s upcoming server CPU, its potential impact on the tech industry, and practical steps you can take to position yourself for this exciting development. So, buckle up as we dive into the world of high-performance computing and explore what’s next for Intel and the broader tech ecosystem.
How Intel’s Clearwater Forest Could Revolutionize Server Computing and Boost Its Foundry Business
Intel’s recent announcement of its Clearwater Forest project has sparked significant interest in the tech industry, promising a potential revolution in server computing and a significant boost to Intel’s foundry business. The project, a sprawling 1,000-acre campus in Chandler, Arizona, is set to house Intel’s most advanced semiconductor manufacturing facility to date, capable of producing chips using the company’s cutting-edge 20A and 18A processes.
The implications of this project are vast. By investing in advanced manufacturing capabilities, Intel is positioning itself to compete with the likes of TSMC and Samsung in the foundry market. This could lead to a surge in domestic semiconductor production, reducing the United States’ reliance on foreign chip supplies and bolstering its technological sovereignty.
Moreover, the Clearwater Forest facility is expected to play a pivotal role in Intel’s efforts to regain its leadership in server computing. The advanced chips produced here could power next-generation servers, offering improved performance, energy efficiency, and security. This could significantly impact data centers worldwide, enabling them to handle increased workloads, reduce operational costs, and enhance data protection.
However, the success of the Clearwater Forest project is not guaranteed. Intel faces stiff competition in the foundry market and must navigate the complex challenges of ramping up advanced manufacturing. Nevertheless, the project represents a significant step forward for Intel and the broader tech industry, potentially reshaping the landscape of server computing and foundry services. As such, all eyes are on Intel as it begins construction on the Clearwater Forest campus, with the world eagerly awaiting the fruits of its labor.
The Server CPU Landscape: Intel vs. AMD
The server CPU market has witnessed a significant shift in recent years, with AMD making substantial inroads against long-time dominant Intel. AMD’s EPYC series, launched in 2017, brought fierce competition to the data center, offering superior core counts and performance per dollar, challenging Intel’s monopoly.
Intel, however, has not been idle in the face of this challenge. The company’s recent struggles, including manufacturing delays and setbacks with its 10nm process, have allowed AMD to gain market share. But Intel has been fighting back with its latest server CPU families, Granite Rapids and Sierra Forest.
Granite Rapids, based on Intel’s 4nm process, is expected to bring significant performance improvements, with up to 56 cores and support for DDR5 memory. It’s designed to tackle the high-core count workloads that AMD’s EPYC processors excel at. Meanwhile, Sierra Forest, Intel’s upcoming single-socket server CPU, promises to deliver high performance in a more power-efficient package, targeting the growing market for sustainable data centers.
Intel’s response to AMD’s challenge is a testament to the dynamic nature of the tech industry. As AMD has pushed the envelope with its server CPUs, Intel has been forced to innovate and adapt. The result is a more competitive market, with both companies driving each other to deliver better, more efficient server CPUs. This competition benefits consumers and businesses alike, as they can choose from a wider range of powerful, reliable, and affordable server solutions.

Introducing Clearwater Forest: Intel’s Many-Core Monster
Introducing Clearwater Forest: Intel’s Many-Core Monster
The Power of Intel 18A: A Manufacturing Turnaround
Exploring Intel’s 18A manufacturing process, its advantages over TSMC’s latest processes, and its potential to help Intel reclaim its manufacturing edge.
Advanced Technologies in Clearwater Forest
In the heart of the tech industry, nestled in the serene Clearwater Forest, lies a semiconductor company that’s pushing the boundaries of innovation. Their latest chips, codenamed ‘Clearwater Forest’, are a testament to the advanced packaging technology and microarchitectural enhancements that are set to redefine the computing landscape.
The Clearwater Forest chips introduce a groundbreaking packaging technology that allows for higher density and improved performance. This is achieved through a process called 3D integration, where multiple layers of silicon are stacked on top of each other, connected by through-silicon vias (TSVs). This not only reduces the footprint of the chip but also significantly improves data transfer rates between different components.
At the core of these chips lies a revolutionary 3D cache, or local cache, that leverages the vertical space to provide a massive boost in cache size. This local cache is designed to sit between the processor and the main memory, acting as a high-speed buffer to reduce latency and improve overall system performance. The 3D cache is organized in a way that allows for efficient data movement, ensuring that the processor always has access to the data it needs, when it needs it.
The Clearwater Forest chips also introduce a new transistor type, codenamed ‘Clearwater Transistor’. This transistor is designed to operate at lower voltages and higher frequencies, providing a significant improvement in power efficiency. The new transistor type is achieved through a combination of advanced materials and manufacturing processes, pushing the limits of what’s possible with traditional silicon.
Lastly, the Clearwater Forest chips feature a novel backside power delivery system. This system delivers power to the chip from the backside, allowing for more efficient power distribution and reduced power losses. This is achieved through a series of through-silicon vias that connect the power delivery network on the backside of the chip to the transistors on the front side. This not only improves power efficiency but also allows for more complex and dense chip designs.
These advanced technologies in the Clearwater Forest chips are a testament to the incredible innovation happening in the semiconductor industry. They promise to deliver significant improvements in performance, power efficiency, and system responsiveness, paving the way for the next generation of computing.
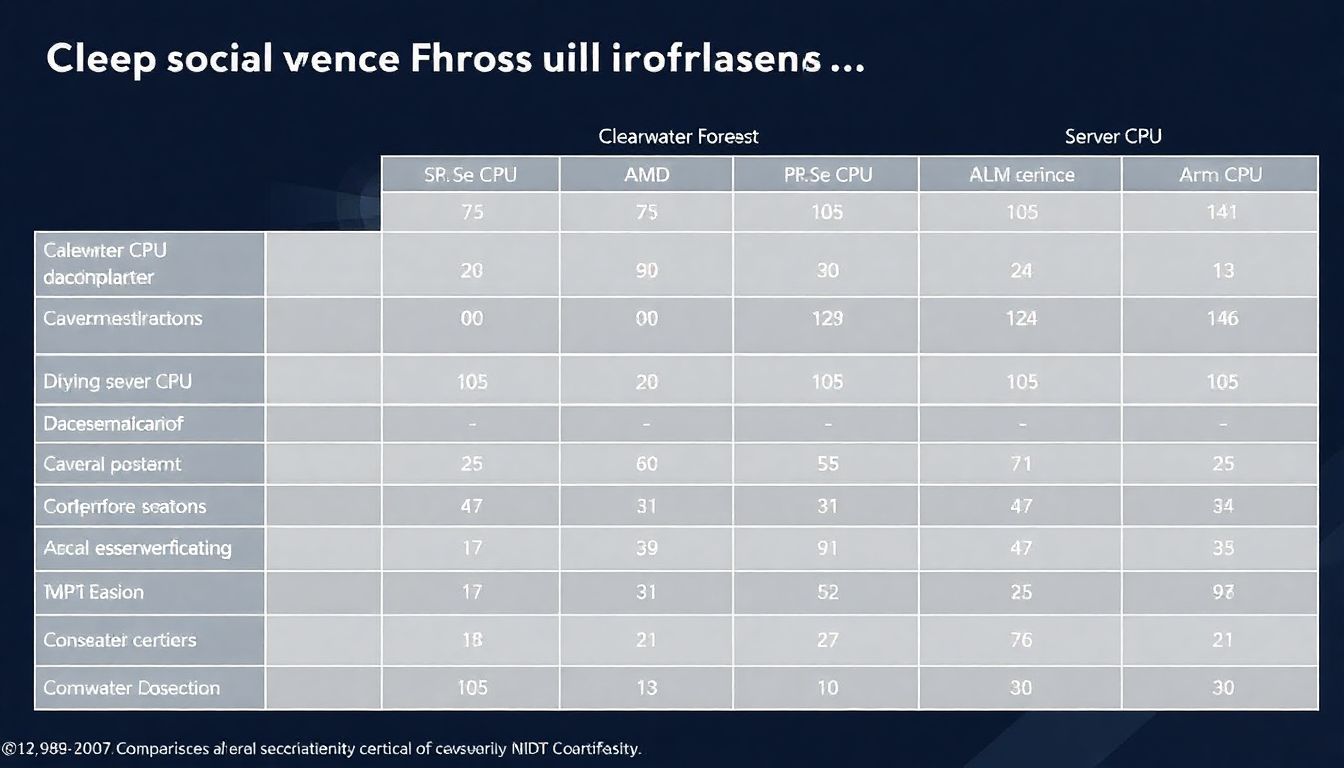
Clearwater Forest vs. Arm-Based Server CPUs
Discuss the growing trend of large cloud companies designing their own Arm server chips, and how Clearwater Forest could make such a move less appealing.

Clearwater Forest: A Showcase for Intel’s Foundry Business
Clearwater Forest: A Showcase for Intel’s Foundry Business
Intel’s Turnaround: Patience Required
Reflect on Intel’s slow and painful turnaround, the importance of Clearwater Forest’s success, and the need for investors to remain patient.
FAQ
What is the significance of Intel’s upcoming monster server CPU in 2025?
What can we expect from this new Intel server CPU in terms of performance?
How will this new CPU impact the data center industry?
What does this announcement mean for Intel’s competitors?
When can we expect more concrete details about this new CPU?
What can data center operators do to prepare for this new CPU?
- assessing their current infrastructure and determining if it’s ready for the expected performance improvements,
- evaluating their workloads to see how they might benefit from the new CPU’s capabilities,
- considering how they might need to update their power and cooling infrastructure to support the new CPU,
- and staying informed about Intel’s announcements and the broader server CPU market.
How might this new CPU impact the cost of cloud computing services?
- offer more powerful instances at the same price,
- reduce the number of servers needed to handle a given workload, leading to potential cost savings,
- or pass on some of the benefits to customers in the form of lower prices or improved service level agreements.
However, it’s also possible that the initial cost of the new CPU could lead to temporary price increases as cloud providers update their infrastructure.
What role might this new CPU play in the development of exascale computing?
How might this new CPU impact the gaming industry?
- create more complex and immersive game worlds,
- improve the performance of online gaming services,
- and develop new cloud gaming technologies that allow players to stream high-quality games without the need for powerful local hardware.
Additionally, the new CPU could help drive innovation in AI and machine learning, which are increasingly important in game development.